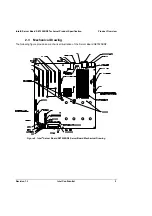
Product Overview
Intel® Server Board SE7520BD2 Technical Product Specification
12
Revision
1.3
2.7.1.6 Processor
Cache
The BIOS enables all levels of processor cache as early as possible during POST. There are no
user options to modify the cache configuration, size or policies. All detected cache sizes are
reported in the SMBIOS Type 7 structures. The largest and highest level cache detected is
reported in BIOS Setup.
2.7.1.7 Hyper-Threading
Technology
Intel
®
Xeon
TM
processors support Hyper-Threading Technology. The BIOS will detect
processors that support this feature and will enable the feature during POST. BIOS Setup
provides an option to selectively enable or disable this feature. The default behavior is enabled.
The BIOS will create additional entries in the ACPI MP tables to describe the virtual processors.
The SMBIOS Type 4 structure will show only the physical processors installed
2.7.2 Multiple
Processor
Initialization
IA32 processors have a microcode-based BSP-arbitration protocol. On reset, all of the
processors compete to become the bootstrap processor (BSP). If a serious error is detected
during a Built-in Self-Test (BIST), that processor will not participate in the initialization protocol.
A single processor that successfully passes BIST is automatically selected by the hardware as
the BSP and starts executing from the reset vector (F000:FFF0h). A processor that does not
perform the role of BSP is referred to as an application processor (AP).
The BSP is responsible for executing the BIOS power-on self-test (POST) and preparing the
machine to boot the operating system. At boot time, the system is in virtual wire mode and the
BSP alone is programmed to accept local interrupts (INTR driven by programmable interrupt
controller (PIC) and non-maskable interrupt (NMI)). For single processor configurations, the
system is put in the virtual wire mode, which uses the local APIC of the processor.
As a part of the boot process, the BSP wakes each AP. When awakened, an AP programs its
Memory Type Range Registers (MTRRs) to be identical to those of the BSP. All APs execute a
halt instruction with their local interrupts disabled. The System Management Mode (SMM)
handler expects all processors to respond to an SMI. If the BSP determines that an AP exists
that is a lower-featured processor or that has a lower value returned by the CPUID function, the
BSP will switch to the lowest-featured processor in the system.
2.7.3 Processor
VRD
The Server Board SE7520BD2 has two VRDs (Voltage Regulator Down) providing the
appropriate voltages to the installed processors. Each VRD is compliant with the VRD 10.1
specification and is designed to support current and next generation Intel® Xeon™ processors
that require up to a sustained maximum of 105 A and peak support of 120 A.
The baseboard supports Flexible Mother Board (FMB) for all Intel® Xeon™ processors with
respect to current requirements and processor speed requirements. FMB is an estimation of the
maximum values the processors will have over their lifetime. The value is only an estimate and
actual specifications for future processors may differ. Currently, the demand per FMB is a
sustained maximum of 105 Amps and a peak support of 120 Amps.