Error Reporting and Handling
Intel® Server Board SE7520BD2 Technical Product Specification
122
Revision
1.3
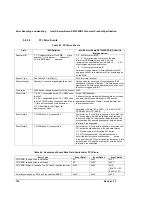
0EAh MEM_ERR_TIMING
0EBh MEM_ERR_REG_CAS_3
0ECh MEM_ERR_NONREG_MIX
0EDh MEM_ERR_CAS_LATENCY
0EEh MEM_ERR_SIZE_NOT_SUPPORTED
0EFh MEM_ERR_POPULATION_ORDER
0F0h SYS_FREQ_ERR
(Flag for Unsupported System Bus Freq)
0F1h DIMM_ERR_CFG_MIX
(Usupported DIMM mix)
0F2h DQS_FAILURE
(indicates DQS failure)
0F3h MEM_ERR_MEM_TEST_FAILURE
(Error code for unsuccessful Memory Test)
0F4h
MEM_ERR_ECC_INIT_FAILURE
(Error code for unsuccessful ECC and Memory
Initialization)
0F5h
MEM_ERR_RCVDLYA_FAILURE
5.3.3.3
POST Error Pause
In case of POST error(s), which occur during system boot-up, the BIOS will stop and wait for the
user to press an appropriate key before booting the OS or entering BIOS Setup.
5.4 Error Logging
5.4.1
Error Sources and Types
One of the major requirements of server management is to correctly and consistently handle
system errors. System errors can be categorized as follows:
•
PCI bus
•
Memory single- and multi-bit errors
•
Sensors
•
Processor internal errors, bus/address errors, thermal trip errors, temperatures and
voltages, and GTL voltage levels
•
Errors detected during POST and logged as ‘POST errors’
Some system errors can be Enabled/Disabled individually (e.g., PCI Errors, FSB Errors and
Memory Errors) by the user in BIOS Setup.
Sensors are managed by the BMC. The BMC is capable of receiving event messages from
individual sensors and logging system events.
The BIOS logs system errors to the SEL. Be aware that error numbers for the same error may
be different depending upon whether the error was logged to the SEL or to the management
module (MM).