7PG2113/4/5/6 Solkor Applications Guide
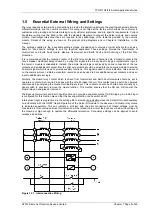
The UK has vast experience of the use of pilot wire differential feeder protection and the UK supply industry
specification on multipair cables, ESI Standard 09-6 is therefore particularly applicable as a reference for pilot
wire requirements.
It should be noted that the voltage between cores in the pilots is limited by the non-linear resistors which are
connected across the summation transformers in the Solkor relays at the ends. Also note that any induced
voltage will be at an equal level per unit length in all cores and screen. Thus it is possible to use pilots with 500v
grade insulation between cores and core to screen. The 5 or 15kV insulation requirement exists only between
‘internal cores and screen’ to the local earth. Similar considerations should be observed at any cable terminations
where standard 500v terminals can be used but the whole terminal block should be mounted on an insulating
baseplate to comply with insulation requirements to the local ground. Terminals should be shrouded and clearly
marked since during a system fault (included a fault on any parallel feeder, not only the protected circuit) the
induced voltage may pose a serious risk to health. Inside of the protection panel, the insulation to local earth and
segregation of wiring for health and safety purposes may be more easily achieved by the use of separate cable
trunking which can be routed independently and clearly marked rather than by the use of special cabling inside of
the panel. Special precautions will be required when terminating or handling pilot connections.
Pilot inter-core capacitance has the effect of shunting the relays in the current balance scheme. As the
capacitance increases a point is reached where the shunt impedance has a significant effect on the relay settings.
This produces a maximum limit for pilot capacitance which can be used with the relay. With the relays in the
Solkor R connection mode the pilot capacitance maximum limit is 2.5
μ
F and with the Solkor Rf connection mode
this limit is 0.8
μ
F. These limits can be increased for the Solkor Rf mode by the use of transformer tappings if the
15kV isolation transformers are used. The limits are 1
μ
F, 2
μ
F and 4
μ
F which impose accompanying pilot LOOP
resistance limits of 1760
Ω
, 880
Ω
and 440
Ω
respectively.
The pilot resistance is used in conjunction with settable padding resistance to achieve the stability biasing of the
relay. The padding resistance must be set in series with the pilot resistance to achieve a standard value. There is
therefore a maximum value for the pilot resistance for which the padding should be set to zero. The maximum
value of pilot LOOP resistance for the Solkor R mode is 1000
Ω
and for the Solkor Rf mode the maximum LOOP
resistance is 2000
Ω
.
When 15kV isolation transformers in the Rf mode the maximum LOOP resistance
will be reduced to 1760
Ω
to compensate for the transformer
winding resistance and if the transformer taps
are used to compensate for the effects of pilot capacitance the maximum LOOP resistance is reduced further to
values of, 880
Ω
and 440
Ω
depending on the tap used.
The actual pilot resistance must be referred through
the transformer at the chosen tap to give an equivalent pilot resistance value to which the padding
should be added.
Thus the padding resistance R = (Sv-Rp)/(2T)
Where Rp = Pilot LOOP resistance
Sv = standard value
=1000
Ω
for Solkor R mode (T=1)
=2000
Ω
for 5kV Solkor Rf mode (without transformers) (T=1)
=1760
Ω
for Solkor Rf with 15kV transformers using tap 1 (T=1)
=880
Ω
for Solkor Rf with 15kV transformers using tap 0.5 (T=0.5)
=440
Ω
for Solkor Rf with 15kV transformers using tap 0.25 (T=0.25)
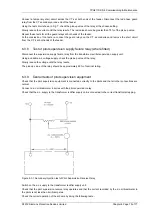
1.6.4 Pilot Supervision
Pilot supervision is used to detect failure of the pilot connection. Open circuit Pilots will lead to a loss of the
balance current from the remote end which will tend towards a differential trip condition. Pilot Supervision is often
applied as standard with the Solkor system but may be considered unnecessary at lower voltages or in an
interconnected system where unnecessary tripping of an un-faulted feeder may be tolerated due to limited
consequences in terms of loss of supply and relatively low probability of pilot damaged or failure when compared
to the additional equipment cost.
The Pilot Supervision system uses DC injection which cannot pass through a transformer. For this reason the
Pilot Supervision must be applied at the pilot side of the 15kV isolation transformers if fitted and therefore the
devices must have an isolation level to suit. The Send End unit and B75 Receive End must have 15kV insulation.
The B22 Supervision Relay and B74 Repeat Relay are not connected to the pilots directly and no special isolation
requirements apply to these devices.
1.6.5 Injection Intertripping
Injection Intertripping is generally difficult to apply successfully in conjunction with Overcurrent Guard relays since
the remote Guard relay will block operations resulting from intertrip injection if the remote end CT current is below
the Guard setting.
©2010 Siemens Protection Devices Limited
Chapter 7 Page 12 of 49