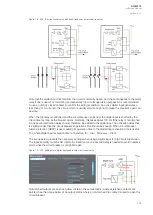
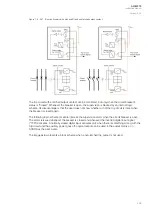
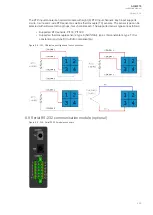
When an I/O module is inserted into the device, the module location affects the naming of the I/O. The
I/O scanning order in the start-up sequence is as follows: the CPU module I/O, Slot C, Slot E, and Slot
F. This means that the digital input channels DI1, DI2 and DI3 as well as the digital output channels
OUT1, OUT2, OUT3, OUT4 and OUT5 are always located in the CPU module. If additional I/O cards
are installed, their location and card type affect the I/O naming.
The figure below presents the start-up hardware scan order of the device as well as the I/O naming
principles.
Figure. 8.1 - 244. AQ-X215 hardware scanning and I/O naming principles.
1. Scan
The start-up system; detects and self-tests the CPU module, voltages, communication and
the I/O; finds and assigns "DI1", "DI2", "DI3", "OUT1", "OUT2", "OUT3", "OUT4" and "OUT5".
2. Scan
Scans Slot A and finds the four channels of the VT module (fixed for AQ-X215). If the VTM is
not found, the device issues an alarm.
3. Scan
Scans Slot B, which should always remain empty in AQ-X215 devices. If it is not empty, the
device issues an alarm.
4. Scan
Scans Slot C, and moves to the next slot if Slot C is empty. If the scan finds an 8DI module
(that is, a module with eight digital inputs), it reserves the designations "DI4", "DI5", "DI6",
"DI7", "DI8", "DI9", "DI10" and "DI11" to this slot. If the scan finds a DO5 module (that is, a
module with five digital outputs), it reserves the designations "OUT6", "OUT7", "OUT8",
"OUT9" and "OUT10" to this slot. The I/O is then added if the type designation code (e.g. AQ-
P215-PH0AAAA-BBC) matches with the existing modules in the device. If the code and the
modules do not match, the device issues and alarm. An alarm is also issued if the device
expects to find a module here but does not find one.
A
AQ
Q-M215
-M215
Instruction manual
Version: 2.04
411