MC96FM204/FM214
April 7, 2016 Ver. 1.8
43
8. Memory
The MC96FM204/FM214 addresses two separate address memory stores: Program memory and Data memory.
The logical separation of Program and Data memory allows Data memory to be accessed by 8-bit addresses,
which makes the 8-bit CPU access the data memory more rapidly. Nevertheless, 16-bit Data memory addresses
can also be generated through the DPTR register.
MC96FM204/FM214 provides on-chip 4k bytes of the ISP type flash program memory, which can be read and
written to. Internal data memory (IRAM) is 256 bytes and it includes the stack area.
8.1 Program Memory
A 16-bit program counter is capable of addressing up to 64k bytes, but this device has just 4k bytes program
memory space.
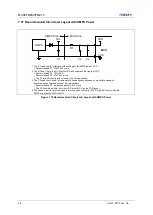
Figure 8-1 shows the map of the lower part of the program memory. After reset, the CPU begins execution from
location 0000H. Each interrupt is assigned a fixed location in program memory. The interrupt causes the CPU to
jump to that location, where it commences execution of the service routine. External interrupt 1, for example, is
assigned to location 000BH. If external interrupt 1 is going to be used, its service routine must begin at location
000BH. If the interrupt is not going to be used, its service location is available as general purpose program
memory. If an interrupt service routine is short enough (as is often the case in control applications), it can reside
entirely within that 8 byte interval. Longer service routines can use a jump instruction to skip over subsequent
interrupt locations, if other interrupts are in use.
Summary of Contents for MC96FM204
Page 17: ...MC96FM204 FM214 April 7 2016 Ver 1 8 17 4 Package Diagram Figure 4 1 20 Pin SOP Package ...
Page 18: ...MC96FM204 FM214 18 April 7 2016 Ver 1 8 Figure 4 2 20 Pin TSSOP Package ...
Page 19: ...MC96FM204 FM214 April 7 2016 Ver 1 8 19 Figure 4 3 16 Pin SOP Package ...
Page 20: ...MC96FM204 FM214 20 April 7 2016 Ver 1 8 Figure 4 4 16 Pin TSSOP Package ...