Section 9
Inspection and Reconditioning
9.10
Replacement pistons are available in STD bore size,
and in 0.25 mm (0.010 in.), and 0.50 mm (0.020 in.)
oversize. Replacement pistons include new piston
ring sets and new piston pins.
Replacement ring sets are also available separately
for STD, 0.25 mm (0.010 in.), and 0.50 mm (0.020 in.)
oversize pistons. Always use new piston rings when
installing pistons. Never reuse old rings.
Some important points to remember when servicing
piston rings:
1. The cylinder bore must be deglazed before
service ring sets are used.
2. If the cylinder bore does not need reboring and if
the old piston is within wear limits and free of
score or scuff marks, the old piston may be
reused.
3. Remove the old rings and clean up the grooves.
Never reuse old rings
.
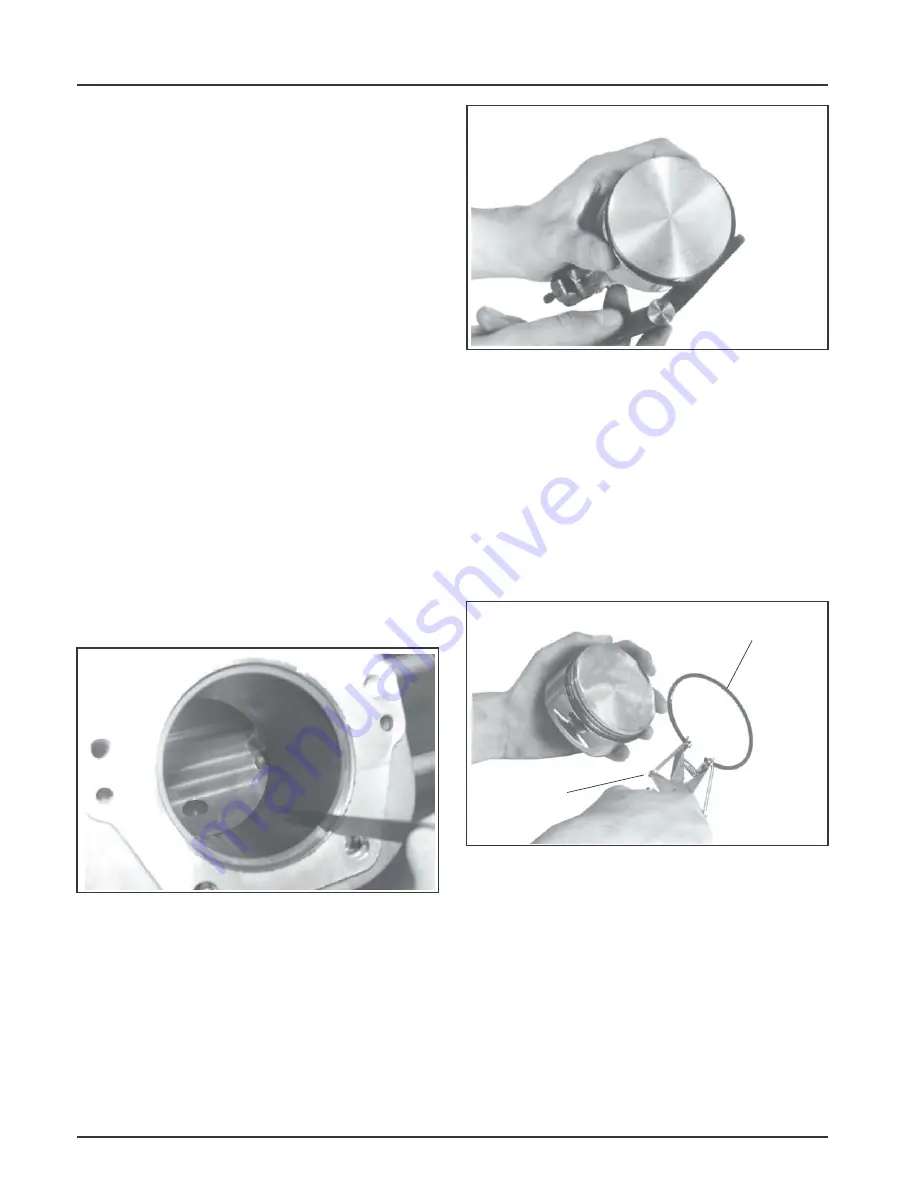
4. Before installing the new rings on the piston,
place the top two rings, each in turn, in its
running area in the cylinder bore and check the
end gap. See Figure 9-9. Compare the ring gap to
the specifications listed in Section 1.
Figure 9-10. Measuring Piston Ring Side
Clearance.
Install New Piston Rings
To install new piston rings, proceed as follows:
NOTE
: Rings must be installed correctly. Ring
installation instructions are usually included
with new ring sets. Follow instructions
carefully. Use a piston ring expander to
install rings. See Figure 9-11. Install the
bottom (oil control) ring first and the top
compression ring last. Refer to Figure 9-12.
Figure 9-11. Installing Piston Rings.
Figure 9-9. Measuring Piston Ring End Gap.
5. After installing the new compression (top and
middle) rings on the piston, check the piston-to-
ring side clearance. Compare the clearance to
specifications listed in Section 1. If the side
clearance is greater than specified, a new piston
must
be used. Refer to Figure 9-10.
Piston Ring
Piston Ring
Expander
















































