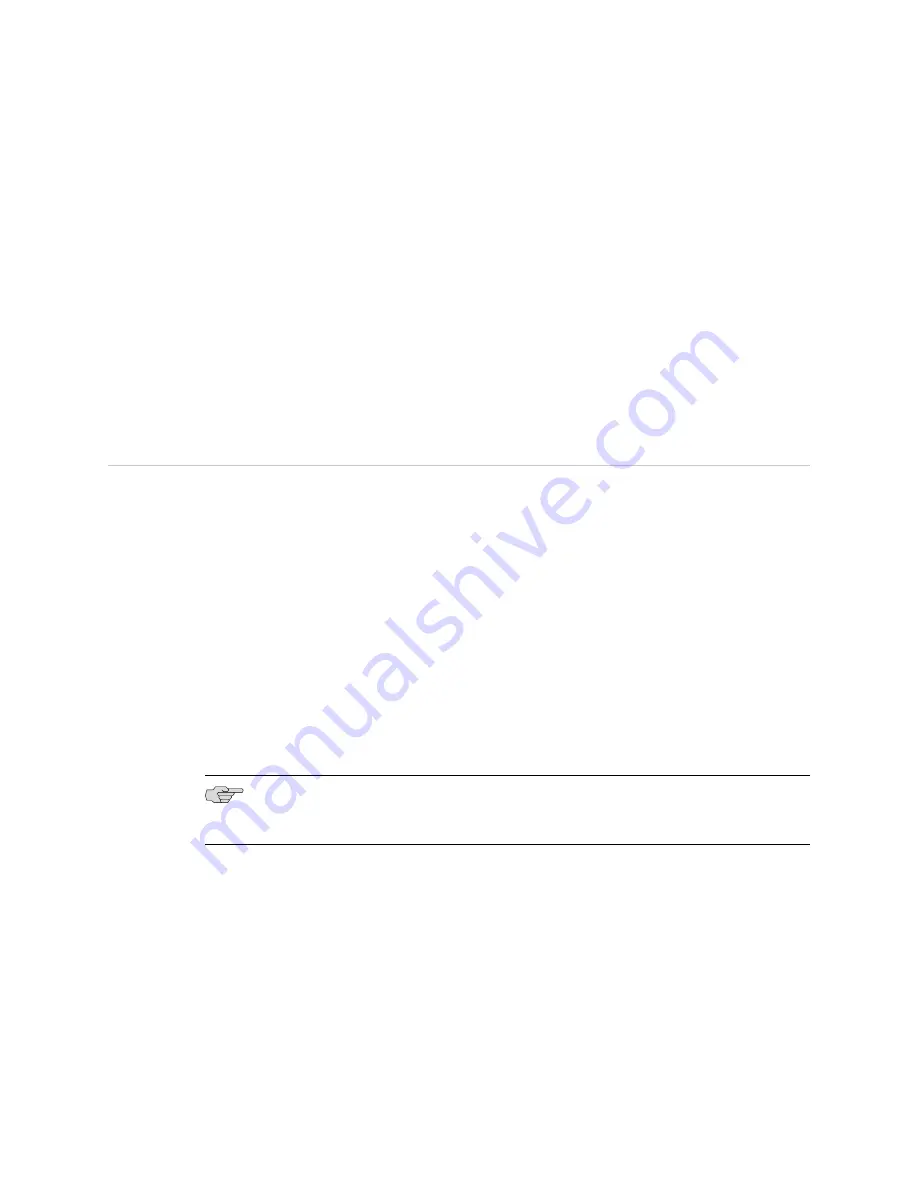
ABR 2-->Router 5-->Router 4
The highest individual cost is 3. ABR 2 subsequently calculates a cost of 3 for the
aggregate 10.1.1.0 to be announced into area 0.
When Router 3 sends traffic to Router 4, it routes the traffic via ABR 2 because ABR 2
advertises a lower cost than does ABR 1. However, this path is not optimal, because
the traffic must traverse Router 3-->Router 7-->ABR 2--> Router 5-->Router 4. The
path through ABR 1, Router 3-->ABR 1-->Router 4 is a better path, even though
ABR 1 advertised a higher aggregate cost.
You can avoid this kind of suboptimal routing by manually configuring a cost for the
aggregate. The summary LSA then announces the configured cost instead of the
automatically calculated cost. Use the
cost
keyword with the
area range
command
to specify a cost for a range of OSPF networks aggregated at an area boundary.
Configuring Authentication
The router supports the following authentication capabilities:
■
Null authentication
■
Simple password authentication
■
MD5 authentication
The MD5 algorithm takes as input a message of arbitrary length and produces a
128-bit
fingerprint
or
message digest
of the input. MD5 is used to create digital
signatures. It is a one-way
hash
function, meaning that it takes a message and converts
it into a fixed string of digits, called a message digest.
When using a one-way hash function, you can compare a calculated message digest
with the message digest that is decrypted by using a public key (password). The key
verifies that the message has not been tampered with. This comparison process is
called a hashcheck.
NOTE:
You must first issue the
address area
command before issuing any other
address
command.
Authentication Requirements
If you configure either simple password or MD5 authentication, the password or
authentication key must be the same on both sides of an adjacency. When you
change the password or key on one side of an established adjacency, you must also
change it on the other side within the dead interval. Doing this enables a hello packet
that has the latest authentication information to be sent before the dead interval
expires. If the packet is not sent within the dead interval, the adjacency breaks down
and is not reestablished until both sides of the adjacency have the same password
or key.
address authentication-key
272
■
Configuring Authentication
JUNOSe 11.0.x IP, IPv6, and IGP Configuration Guide
Содержание IGP - CONFIGURATION GUIDE V11.1.X
Страница 6: ...vi...
Страница 8: ...viii JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 18: ...xviii List of Figures JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 20: ...xx List of Tables JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 26: ...2 Internet Protocol JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 148: ...Set clauses set local pref 400 See show route map 124 Monitoring IP JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 228: ...204 Internet Protocol Routing JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 264: ...240 Monitoring RIP JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 438: ...414 Monitoring IS IS JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 439: ...Part 3 Index Index on page 417 Index 415...
Страница 440: ...416 Index JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
Страница 454: ...430 Index JUNOSe 11 0 x IP IPv6 and IGP Configuration Guide...
















































