l
Results of the preceding troubleshooting procedure
l
Configuration files, log files, and alarm files of the Router
----End
Relevant Alarms and Logs
Relevant Alarms
None.
Relevant Logs
None.
12.2.4 NAT Traversal in IPSec Fails
Common Causes
This fault is commonly caused by one of the following:
l
The link is faulty.
l
Data flows are not forwarded from a specified interface.
l
Data flows do not match the ACL.
l
The settings of IPSec proposals at both ends of the IPSec tunnel are different or ESP is not
used.
l
The settings of IPSec policies at both ends of the IPSec tunnel do not match. For example,
the IPSec negotiation modes are different or the Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) settings
are different.
l
The ACLs referenced by IPSec policies at both ends do not mirror each other.
l
The settings of IKE proposals at both ends of the IPSec tunnel are different.
l
The settings of IKE peers at both ends of the IPSec tunnel are incorrect. For example, the
aggressive mode is not used, IKE versions are different, IP addresses of IKE peers do not
match, names of IKE peers do not match, NAT traversal is disabled, or the IKE peer ID
type is not name.
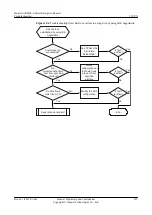
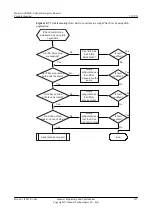
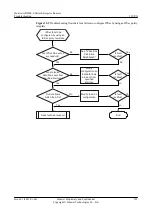
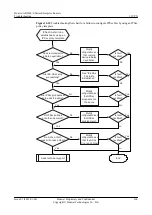
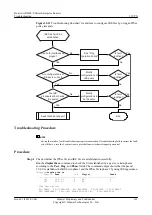
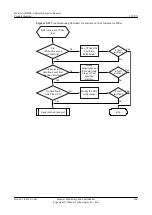
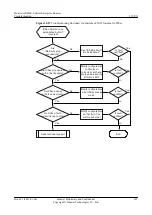
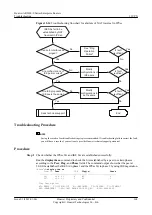
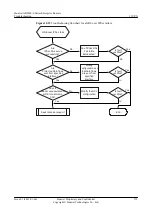
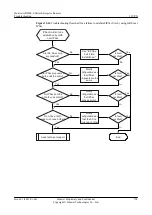
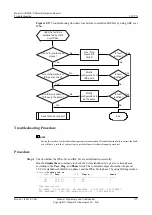
Troubleshooting Flowchart
shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Huawei AR2200-S Series Enterprise Routers
Troubleshooting
12 VPN
Issue 01 (2012-01-06)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
365