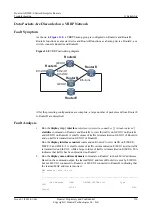
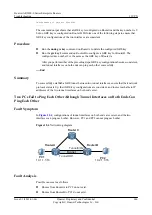
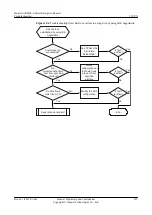
1.
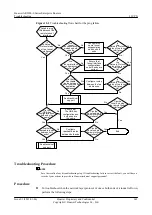
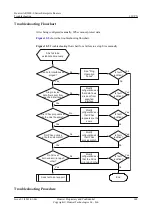
Check that interfaces on both ends of a tunnel use the same tunnel encapsulation mode.
Run the
display this interface
command in the tunnel interface view to check whether
interfaces on both ends use the same tunnel encapsulation mode. If
Tunnel protocol/
transport GRE/IP
is displayed, the tunnel encapsulation mode is GRE.
–
If the two interfaces use different tunnel encapsulation modes, run the
tunnel-
protocol
command in the tunnel interface view to reconfigure the tunnel
encapsulation mode.
NOTE
After you reconfigure the tunnel encapsulation mode, reconfigure the tunnel source and
destination addresses because configurations of the original source and destination
addresses were lost.
–
If the two interfaces use the same tunnel encapsulation mode, go to step 2.
2.
Check that IP, tunnel source, and tunnel destination addresses are configured for
interfaces on both ends of the tunnel. A tunnel source address and a tunnel destination
address uniquely identify a tunnel.
Check whether the local tunnel source address is the peer tunnel destination address
and the local tunnel destination address is the peer tunnel source address. If not, no
tunnel can be established between the two interfaces.
Run the
display this
command in the tunnel interface view to check the interface
configuration. Ensure that the local tunnel source address is the peer tunnel destination
address and the local tunnel destination address is the peer tunnel source address.
–
If the tunnel source and destination addresses are incorrect, reconfigure the
addresses in the tunnel interface view.
–
If the tunnel source and destination addresses are correct, go to step 3.
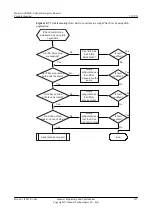
3.
Check that reachable routes exist between the tunnel source and destination addresses.
If the interface configurations on both ends are correct but the tunnel status is still
Down, check whether reachable routes exist between interfaces on both ends of the
tunnel:
–
If the tunnel is established between two indirectly connected interfaces, check
whether reachable routes exist between the two interfaces.
–
If the tunnel is established between two directly connected interfaces, routes are
not required.
Run the
display ip routing-table
command to view the IP routing table. If the IP
routing table is correct, run the
display fib
command to check the forwarding table
(FIB table) and check whether data can be forwarded correctly. Routing information
in the FIB table must be consistent with that in the routing table.
–
If no reachable route exists between the tunnel source and destination addresses,
configure static routes or a dynamic routing protocol to ensure that reachable routes
exist between the tunnel source and destination addresses.
–
If there are reachable routes between the tunnel source and destination addresses
but the fault persists, go to step 4.
4.
Collect the following information and contact Huawei technical support personnel.
–
Results of the preceding troubleshooting procedure
–
Configuration file, log file, and alarm file of the device
Huawei AR2200-S Series Enterprise Routers
Troubleshooting
12 VPN
Issue 01 (2012-01-06)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
343