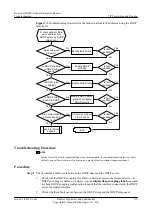
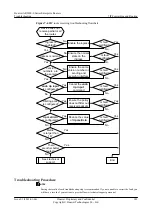
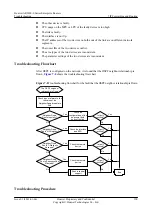
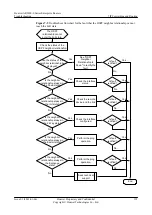
Procedure
Step 1
Check that the incoming interface is enabled with RIP.
The
network
command is used to specify the interface network segment. Only the interface
enabled with RIP can receive and send the RIP routing information.
Run the
display current-configuration
configuration rip
command to check information
about the network segment where RIP is enabled. Check whether the outgoing interface is
enabled.
The network address enabled by the
network
command must be that of the natural network
segment.
Step 2
Check that the incoming interface works normally.
Run the
display interface
command to check the operating status of the incoming interface:
l
If the current physical status of the interface is Down or Administratively Down, RIP cannot
receive any route from the interface.
l
If the current protocol status of the interface is Down, the cost of routes learnt by RIP from
the interface changes to 16, and then is deleted.
Therefore, ensure the normal status of the interface.
Step 3
Check that the version number sent by the peer matches with that received on the Local Interface.
By default, the interface sends only RIP-1 packets, but can receive both RIP-1 and RIP-2 packets.
If the version number of the incoming interface and that of the RIP packet are different, RIP
routing information may not be received correctly.
Step 4
Check whether the
undo rip input
command is configured on the incoming interface.
The
rip input
command enables a specified interface to receive RIP packets.
The
undo rip input
command disables a specified interface from receiving RIP packets.
If the
undo rip input
command is configured on the incoming interface, all the RIP packets
from the interface cannot be processed. Therefore, the routing information cannot be received.
Step 5
Check whether a policy used to filter received RIP routes is configured.
The
filter-policy import
command is used to filter the received RIP routes. If an ACL is used,
run the
display current-configuration
configuration acl-basic
command to view whether the
RIP routes learned from the neighbor are filtered. If the IP-Prefix list is used to filter routes, the
display ip ip-prefix
command is used to check the configured policy.
If a routing policy is set to filter routes, it must be configured correctly.
Step 6
Check whether the incoming interface is configured with the
rip metricin
command and if the
metric is larger than 16.
The
rip metricin
command is used to set the metric that is added to a route when the interface
receives a RIP packet.
If the metric exceeds 16, the route is regarded as unreachable and is not added to the routing
table.
Step 7
Check whether the metric of the received routes is larger than 16.
Huawei AR2200-S Series Enterprise Routers
Troubleshooting
7 IP Forwarding and Routing
Issue 01 (2012-01-06)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
184