6 inTeRRuPT COnTROlleR (iTC)
S1C17624/604/622/602/621 TeChniCal Manual
Seiko epson Corporation
6-3
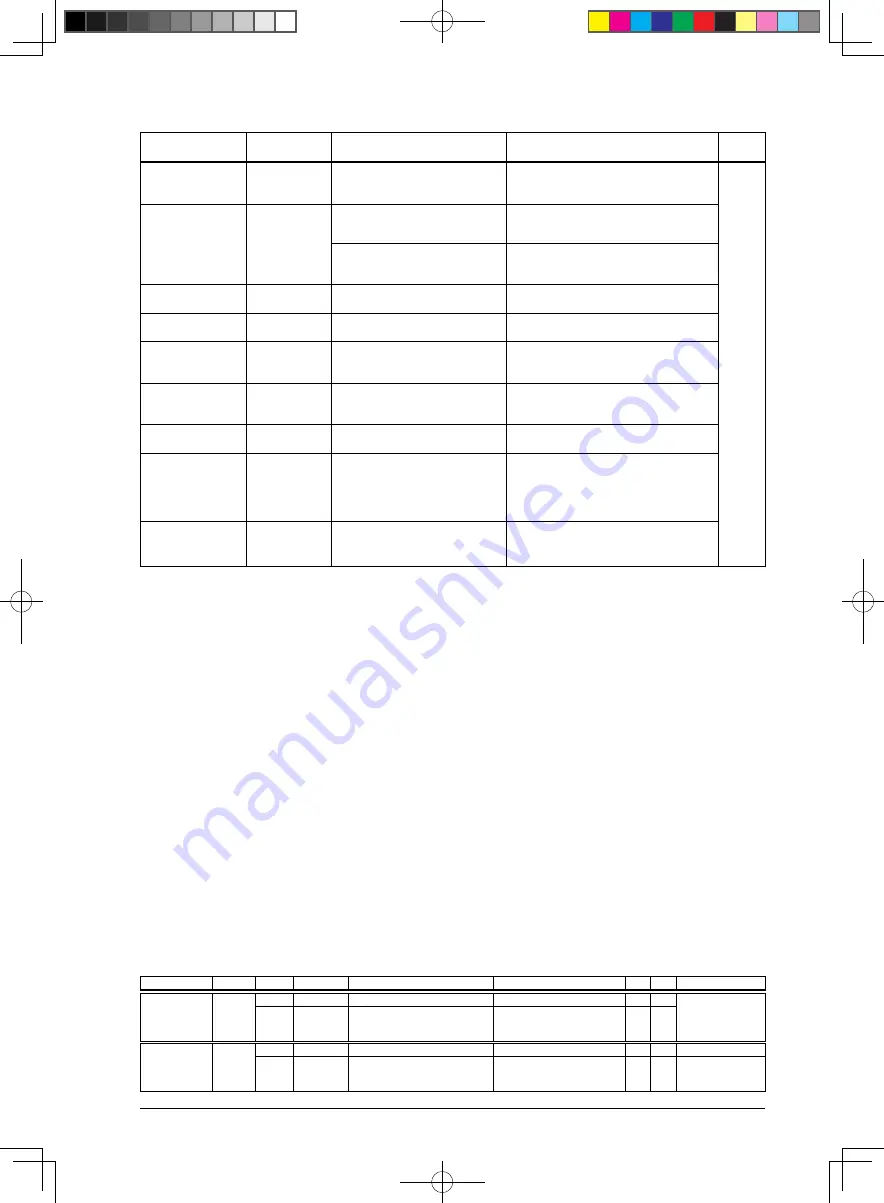
Vector no.
Software interrupt no.
Vector address
hardware interrupt name
Cause of hardware interrupt
Priority
16 (0x10)
TTBR + 0x40
UART Ch.0 interrupt
• Transmit buffer empty
• Receive buffer full
• Receive error
17 (0x11)
TTBR + 0x44
I
2
C Slave (I2CS) interrupt
• Transmit buffer empty
• Receive buffer full
• Bus status
UART Ch.1 interrupt
• Transmit buffer empty
• Receive buffer full
• Receive error
18 (0x12)
TTBR + 0x48
SPI Ch.0 interrupt
• Transmit buffer empty
• Receive buffer full
19 (0x13)
TTBR + 0x4c
I
2
C Master (I2CM) interrupt
• Transmit buffer empty
• Receive buffer full
20 (0x14)
TTBR + 0x50
IR remote controller (REMC)
interrupt
• Data length counter underflow
• Input rising edge detected
• Input falling edge detected
21 (0x15)
TTBR + 0x54
16-bit PWM timer (T16A2) Ch.1
interrupt
(S1C17624/604)
• Compare A/B
• Capture A/B
• Capture A/B overwrite
22 (0x16)
TTBR + 0x58
A/D converter (ADC10) interrupt
• Conversion completion
• Conversion result overwrite
23 (0x17)
TTBR + 0x5c
R/F converter (RFC) interrupt
• Reference oscillation completion
• Sensor A oscillation completion
• Sensor B oscillation completion
• Time base counter overflow error
• Measurement counter overflow error
24 (0x18)
TTBR + 0x60
reserved
–
:
:
:
:
↓
31 (0x1f)
TTBR + 0x7c
reserved
–
Low
*
1
*
1 When the same interrupt level is set
*
2 Either reset or NMI can be selected as the watchdog timer interrupt with software.
Vector numbers 4 to 23 are assigned to the maskable interrupts supported by the S1C17624/604/622/602/621.
interrupts that share an interrupt vector
Interrupt vector numbers 7, 10, and 17 are shared with two different interrupt modules.
Interrupt vector 7: Clock timer (CT) and real-time clock (RTC) (S1C17624/604)
Interrupt vector 10: LCD driver (LCD) and 16-bit PWM timer (T16A2) Ch.0 (S1C17624/604)
Interrupt vector 17: I
2
C slave (I2CS) and UART Ch.1
The interrupt signals from the two modules are input to the ITC through an OR gate. When using the two inter-
rupts, check if which interrupt has occurred by reading the interrupt flags in both modules.
The two modules cannot be set to different interrupt level, as they use the same interrupt vector.
Vector table base address
The S1C17624/604/622/602/621 allows the base (starting) address of the vector table to be set using the MISC_
TTBRL and MISC_TTBRH registers. “TTBR” described in Table 6.2.1 means the value set to these registers.
After an initial reset, the MISC_TTBRL and MISC_TTBRH registers are set to 0x8000. Therefore, even when
the vector table location is changed, it is necessary that at least the reset vector be written to the above address.
Bits 7 to 0 in the MISC_TTBRL register are fixed at 0, so the vector table starting address always begins with a
256-byte boundary address.
Vector Table address low/high Registers (MiSC_TTBRl, MiSC_TTBRh)
Register name address
Bit
name
Function
Setting
init. R/W
Remarks
Vector Table
address low
Register
(MiSC_TTBRl)
0x5328
(16 bits)
D15–8 TTBR[15:8] Vector table base address A[15:8]
0x0–0xff
0x80 R/W
D7–0 TTBR[7:0]
Vector table base address A[7:0]
(fixed at 0)
0x0
0x0
R
Vector Table
address high
Register
(MiSC_TTBRh)
0x532a
(16 bits)
D15–8 –
reserved
–
–
–
0 when being read.
D7–0 TTBR[23:16] Vector table base address
A[23:16]
0x0–0xff
0x0 R/W
















































