Level Two Interface
ARM DDI 0363E
Copyright © 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved.
9-26
ID013010
Non-Confidential, Unrestricted Access
•
There is no TCM present. The mapping of bus addresses to
ARUSERS
and
ARADDRS
is determined when the processor is integrated. You must understand this mapping to use
of the AXI-slave interface within your system.
9.6.2
Cache RAM access
This section contains the following:
•
Memory map when accessing the cache RAMs
•
Data RAM access
on page 9-27
•
Tag RAM access
on page 9-29
•
Dirty RAM access
on page 9-31.
•
Other examples of accessing cache RAMs
on page 9-32
Memory map when accessing the cache RAMs
The memory maps for the data and instruction caches have the same format. Because the
instruction cache does not have a dirty RAM, accesses to it generate the SLVERR error
response.
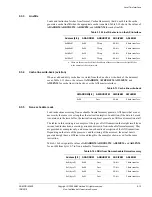
Table 9-29, Table 9-30, and Table 9-31 on page 9-27 show the chip-select decodes for selecting
the cache RAMs in the processor.
Table 9-29 Cache RAM chip-select decode
Inputs
RAM selected
ARUSERS[3:0]
ARADDRS[22:19]
0100
0000
Instruction cache data RAM
0100
0001
Instruction cache tag RAM
0100
0010
Not used, generates an error
0100
0011
Not used, generates an error
0100
ARADDRS[22:21]
!= 00
Not used, generates an error
1000
0000
Data cache data RAM
1000
0001
Data cache tag RAM
1000
0010
Data cache dirty RAM
1000
0011
Not used, generates an error
1000
ARADDRS[22:21]
!= 00
Not used, generates an error
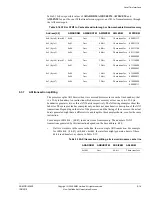
Table 9-30 Cache tag/valid RAM bank/address decode
Inputs
RAM bank
selected
Cache
way
ARADDRS[18:15]
0001
Bank 0
0