System Control Coprocessor
ARM DDI 0363E
Copyright © 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved.
4-45
ID013010
Non-Confidential, Unrestricted Access
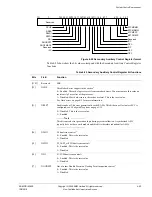
Table 4-26 shows how the bit values correspond with the Coprocessor Access Register
functions.
To access the Coprocessor Access Register, read or write CP15 with:
MRC p15, 0, <Rd>, c1, c0, 2 ; Read Coprocessor Access Register
MCR p15, 0, <Rd>, c1, c0, 2 ; Write Coprocessor Access Register
4.2.18
Fault Status and Address Registers
The processor reports the status and address of faults that occur during its operation. For both
data and instruction faults there are two
Fault Status Registers
(FSRs) and one
Fault Address
Register
(FAR).
Fields within the Data and Instruction FSRs indicate the priority and source of a fault and the
validity of the address in the corresponding FAR. Table 4-27 shows this encoding for the FSRs.
All other encodings for these FSR bits are Reserved.
c5, Data Fault Status Register
The
Data Fault Status Register
(DFSR) holds status information regarding the source of the last
data abort.
Table 4-26 Coprocessor Access Register bit functions
Bits
Field Function
[31:28]
Reserved
SBZ.
[27:0]
cp<n>
a
Defines access permissions for each coprocessor.
Access denied is the reset condition, and is the behavior for non-existent coprocessors.
b00 = Access denied. Attempts to access generates an Undefined exception.
b01 = Privileged mode access only
b10 = Reserved
b11 = Privileged and User mode access.
Access permissions for the FPU are set by fields cp10 and cp11. For all other
coprocessor fields, the value is fixed to b00.
a. n is the coprocessor number between 0 and 13.
Table 4-27 Fault Status Register encodings
Priority
Sources
FSR
[10,3:0]
FAR
Highest
Alignment
0b00001
Valid
Background
0b00000
Valid
Permission
0b01101
Valid
Precise External Abort
0b01000
Valid
Imprecise External Abort
0b10110
Unpredictable
Precise Parity/ECC Error
0b11001
Valid
Imprecise Parity/ECC Error
0b11000
Unpredictable
Lowest
Debug Event
0b00010
Unchanged