Debug
ARM DDI 0363E
Copyright © 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved.
11-2
ID013010
Non-Confidential, Unrestricted Access
11.1
Debug systems
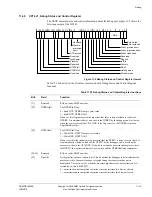
The Cortex-R4 processor is one component of a debug system. Figure 11-1 shows a typical
system.
Figure 11-1 Typical debug system
This typical system has three parts, described in the following sections:
•
Debug host
•
Protocol converter
•
Debug target
.
11.1.1
Debug host
The debug host is a computer, for example a personal computer, running a software debugger
such as RealView
™
Debugger. The debug host enables you to issue high-level commands such
as setting breakpoint at a certain location, or examining the contents of a memory address.
11.1.2
Protocol converter
The debug host connects to the processor development system using an interface such as
Ethernet. The messages broadcast over this connection must be converted to the interface
signals of the debug target. A protocol converter performs this function, for example, RealView
ICE.
11.1.3
Debug target
The debug target is the lowest level of the system. An example of a debug target is a
development system with a Cortex-R4 test chip or a silicon part with a Cortex-R4 macrocell.
The debug target must implement some system support for the protocol converter to access the
processor debug unit using the
Advanced Peripheral Bus
(APB) slave port.
The debug unit enables you to:
•
stall program execution
•
examine the internal state of the processor and the state of the memory system
•
resume program execution.
Host computer running RealView Debugger
Debug
host
For example, RealView ICE
Development system containing
Cortex-R4 processor
Debug
target
Protocol
converter