Level Two Interface
ARM DDI 0363E
Copyright © 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved.
9-25
ID013010
Non-Confidential, Unrestricted Access
9.6.1
TCM RAM access
Table 9-27 shows the decode of the
ARUSERS[3:0]
signal, and the state of the address signals
for accessing the TCM RAMs. The table also shows the
SLBTCMSB
configuration input signal
that determines the address bit that is used, either:
•
ARADDRS[3]
•
ARADDRS[MSB]
, see Table 9-28.
In Table 9-27
ARADDRS[MSB]
means the most significant address bit for the TCM RAM, and
Table 9-28 shows the MSB bit for the different TCM RAM sizes.
ARADDRS[22:3]
indicates the address of the doubleword within the TCM that you want to
access. If you are accessing a TCM that is smaller than the maximum 8MB, then it is possible
to address a doubleword that is outside of the physical size of the TCM.
An access to the TCM RAMs is given a SLVERR error response if:
•
It is outside the physical size of the targeted TCM RAM, that is, bits of
ARADDRS[22:MSB+1]
are non-zero.
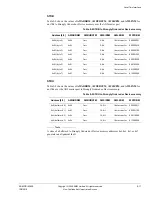
Table 9-27 TCM chip-select decode
BTCM ports
ARUSERS[3:0]
ARADDRS[3]
ARADDRS[MSB]
SLBTCMSB
RAM selected
Don’t care
0001
-
-
-
ATCM
1
0010
-
-
-
B0TCM
2
0010
0
-
0
B0TCM
2
0010
1
-
0
B1TCM
2
0010
-
0
1
B0TCM
2
0010
-
1
1
B1TCM
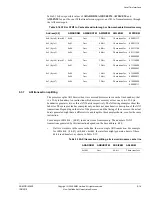
Table 9-28 MSB bit for the different TCM RAM sizes
TCM size
ARADDRS[MSB]
4KB
[11]
8KB
[12]
16KB
[13]
32KB
[14]
64KB
[15]
128KB
[16]
256KB
[17]
512KB
[18]
1MB
[19]
2MB
[20]
4MB
[21]
8MB
[22]