Introduction
ARM DDI 0363E
Copyright © 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved.
1-5
ID013010
Non-Confidential, Unrestricted Access
1.3.1
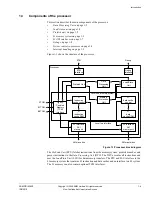
Data Processing Unit
The DPU holds most of the program-visible state of the processor, such as general-purpose
registers, status registers and control registers. It decodes and executes instructions, operating
on data held in the registers in accordance with the ARM Architecture. Instructions are fed to
the DPU from the PFU through a buffer. The DPU performs instructions that require data to be
transferred to or from the memory system by interfacing to the LSU. See Chapter 2
Programmer’s Model
for more information.
Floating Point Unit
The
Floating Point Unit
(FPU) is an optional part of the DPU which includes the VFP register
file and status registers. It performs floating-point operations on the data held in the VFP register
file. See Chapter 12
FPU Programmer’s Model
for more information.
1.3.2
Load/store unit
The LSU manages all load and store operations, interfacing with the DPU to the TCMs, caches,
and L2 memory interfaces.
1.3.3
Prefetch unit
The PFU obtains instructions from the instruction cache, the TCMs, or from external memory
and predicts the outcome of branches in the instruction stream. See Chapter 5
Prefetch Unit
for
more information.
Branch prediction
The branch predictor is a global type that uses history registers and a 256-entry pattern history
table.
Return stack
The PFU includes a 4-entry return stack to accelerate returns from procedure calls. For each
procedure call, the return address is pushed onto a hardware stack. When a procedure return is
recognized, the address held in the return stack is popped, and the prefetch unit uses it as the
predicted return address.
1.3.4
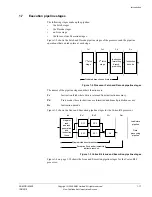
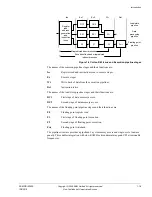
L1 memory system
The processor L1 memory system includes the following features:
•
separate instruction and data caches
•
flexible TCM interfaces
•
64-bit datapaths throughout the memory system
•
MPU that supports configurable memory region sizes
•
export of memory attributes for L2 memory system
•
parity or ECC supported on local memories.
For more information of the blocks in the L1 memory system, see:
•
Instruction and data caches
on page 1-6
•
Memory Protection Unit
on page 1-6
•
TCM interfaces
on page 1-6
•
Error correction and detection
on page 1-7.