DBS9900 User’s Manual
DBS9900 Registers
6-3
82-28993 Revision 01
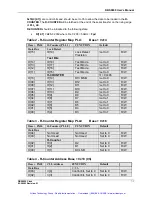
6.1 ID REGISTER 0x00 Read Only
Logical Address Register
The ID REGISTER indicates the ANALOGIC manufacturer’s code and the status of the Mode
Select Jumper (A32 or A24).
Jumper JP1
MODE
ID REGISTER
Value
Pins 1&2 jumpered
A32
0xDFF5
Pins 2&3 jumpered
A24
0xCFF5
The Logical Address Register shares the same address as the ID Register and may only be
loaded during the Dynamic configuration process. The contents of the Logical Address Register
cannot be read back. // say more here about logical address? //
6.2 DEVICE TYPE REGISTER
The DEVICE TYPE REGISTER
(0x02), READ only, indicates the type of memory requirements
as defined in the VXI specifications: the device type code, and the revision level of the PCB. The
value will be 0x
m
21
r
, where
m
is dependent on the memory requirements of the DBS9900 (with
any daughter boards installed) and
r
is the revision level of the printed circuit board (PCB).
The Device Type Register contains a 4-bit field to define the memory size requirements of the
device. This is the value
m
defined in the VXI spec. Four pins on the daughter board connector
are used to request an
m
value from the VXI bus as if the device were in A32 mode. The
DBS9900 will compare the
m
values for the two daughter board modules and select the lowest
(largest amount of memory) non-zero value of
m
for this bit field. If no module is present, resistors
will force these pins to ground, indicating that there is no memory required on this module.
Each daughter board module will have a JTAG port that will be a communication port to a
continuous JTAG chain for programming and testing any ISP programmable devices that may be
resident on the modules. Programming the ISP devices can be accomplished via the JTAG
register inside the VXI interface PLD or via the ByteBlaster™ header on the DBS9900. The only
exception will be the VXI interface PLD itself, which will be configured during power-up via an
EPROM device and which can be programmed via a separate ByteBlaster header as well.
Each daughter board module will have a small serial EEPROM that will contain serial number,
PCB revision number, firmware revision numbers, calibration data, etc. The size of the EEPROM
is 128 words by 16 bits.
Any functions that are repeated among modules will be defined if possible at the same address
with the same bit field. This includes the JTAG and EEPROM ports, clock divisor, trigger select
register, etc. The module select register will map these registers into the device dependent
register space. This allows for some commonality of low-level register control software.
The interface clock will extend to the daughter board for the purpose of I/O and serial data
transfers to DACs and relays. The clock will operate in a burst mode only for the duration of the
VXI bus cycle to reduce analog noise. The interface clock, data, control and address busses will
all remain static when the DBS9900 is not engaged in data bus transfers or an interrupt
acknowledge cycle. These busses will also be buffered as they enter the daughter board to
reduce noise while the VXI bus is accessing the adjacent channel.
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com