Page - 36/95
AEMZP0BA - EPS-AC0 - User Manual
ESD happens when there is a rapid transfer from a charged part to another. This
rapid transfer has, in turn, two important effects:
1) It can determine, by induction, disturbs on the signal wiring and thus create
malfunctions. This effect is particularly critical in modern machines, with CAN
Bus communications, which are spread everywhere on the truck and which
carry critical information.
2) In the worst case and when the amount of charge is very high, the discharge
process can determine failures in the electronic devices; the type of failure can
vary from an intermittently malfunction to a completely failure of the electronic
device.
Three ways can be followed to prevent damages from ESD:
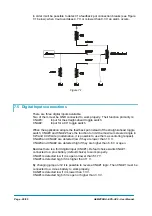
1) INSULATION: To prevent the controller from ESD, it is necessary to consider
that the operator is most of the time the source of ESD. When it gets in touch
with a device on the dashboard having metallic head terminal, the accumulated
charge will be directed from the head terminal to the wires of the device towards
the other units in the truck (e.g. the CAN Bus wires or the wires of the stepper
motor on the dashboard could be the transmission mean). As consequence a
huge inrush current will be generated getting the controller cut off or damaged.
U
To prevent ESD risk it is necessary to avoid that the devices connected to the
CAN communication system have exposed metallic head terminals. The
operator shall not get in touch with any metallic part of the devices CAN Bus
connected.
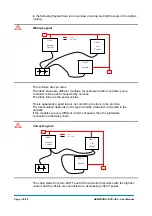
2) GROUNDING: when a complete isolation cannot be achieved, a good
grounding can divert the discharge current trough a “safe” path; the frame of a
truck can work like a “local earth ground”, absorbing excess charge.
U
It is strongly suggested to connect to the truck frame all the parts of the truck
that can get in touch with the operator (who is most of the time the source of
ESD). For example, we strongly suggest to connect the stepper motor frame
to the truck frame.
3) PREVENTION: Another important issue is the storing and handling of ESD-
sensitive electronic parts. Then, ensure the operator is grounded; test grounding
devices on a daily basis for correct functioning. This precaution is particularly
important during controller handling in the storing and installation phase.
Use anti-static containers when transferring ESD-sensitive material.
8.10 Fighting the dither
In Closed Loop application with potentiometers, the quantum nature of the Analog to
Digital conversion, generates dither on the steered wheel. This is a continuous
rolling of the steered wheel from a little bit right to a little bit left around the
commanded position. Obviously, both the potentiometers (SP POT and FB POT)
have noise and contribute to the problem.
There are some countermeasures to reduce or neutralize the dither.
Summary of Contents for EPS-AC0
Page 23: ...AEMZP0BA EPS AC0 User Manual Page 23 95 6 2 EPS AC0 Stepper Motor diagram Figure 6 2...
Page 24: ...Page 24 95 AEMZP0BA EPS AC0 User Manual 6 3 EPS AC0 Twin pot diagram Figure 6 3...
Page 55: ...AEMZP0BA EPS AC0 User Manual Page 55 95 12 3 2 RTC with Encoder and Feedback pot Figure 12 3...