Manual 35018V1
505XT Digital Control System for Steam Turbines
Woodward
186
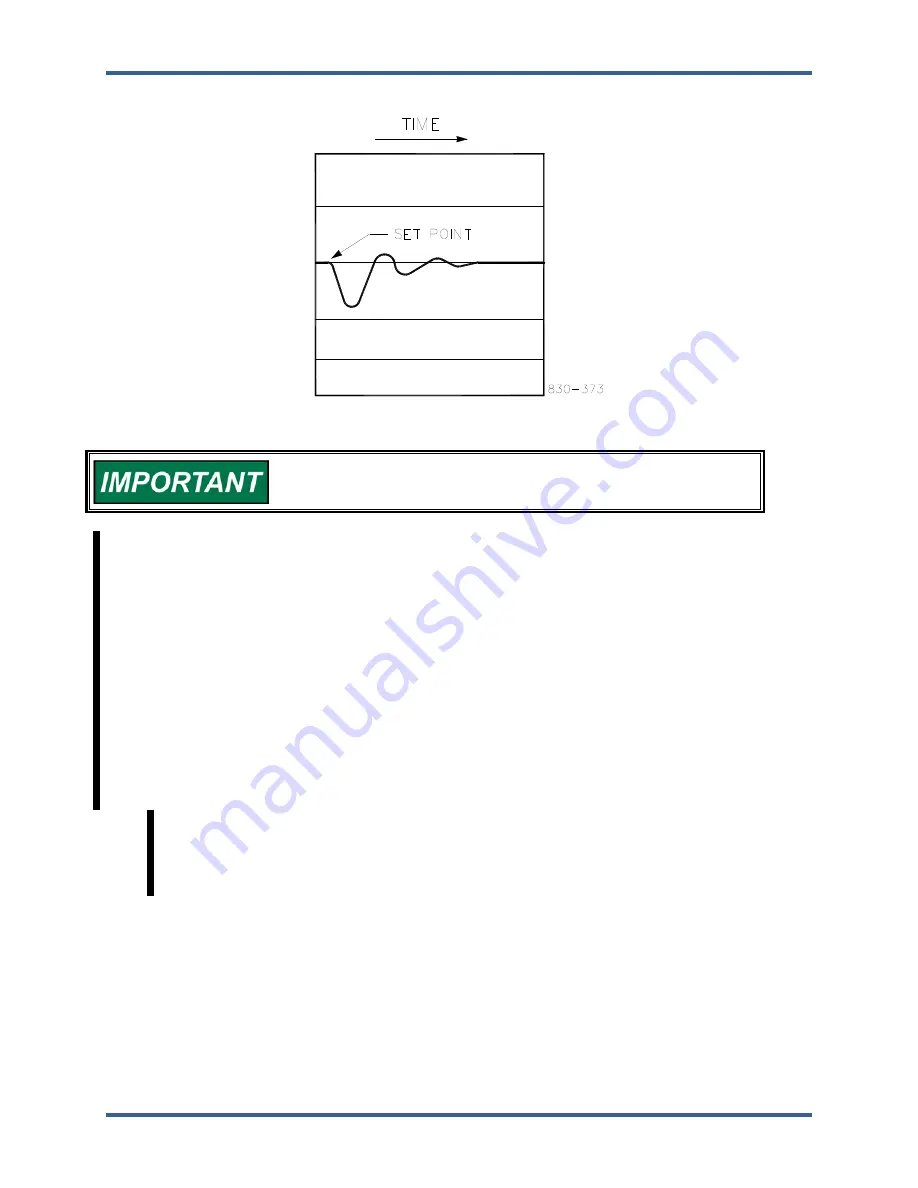
Figure 5-33 shows the typical response to a load change when the dynamics are optimally adjusted.
Figure 5-33. Typical Response to Load Change
For additional information on PID settings, refer to Volume 2.
Automated PID Dynamic Optimizer
The Automated PID Dynamic Optimizer is a routine which allows the control to automatically analyze the
system and calculate the P, I, and D terms. The PID Optimizer routine can be initiated from the controller
Dynamics Optimizer screen and will provide reasonable and stable results. To calculate optimized system
dynamics, small and progressively larger adjustments are made to the valve demand in order to measure
the turbine system. The optimizer routine remains within user specified process and valve movement
limits to ensure that the turbine system remains within acceptable operating limits.
By running the PID Optimizer, the resulting dynamics provide the following benefits:
1) Improved system response to events such as load changes and load rejection
2) Tighter control at the setpoint
3) Response behavior which matches the control loop and application (offline speed control vs load
control, etc.)
4) Improved system diagnostics. The routine provides insight into turbine system control problems
outside of PID tuning and can help to identify them. Some examples include:
a. Non-Linear turbine response due to poppet staging or slew rate limited valve response
b. High system dead-time
c. High
signal
noise
d. Response time variation due to high system friction, loose linkage, or coupling, varying
hydraulic pressure, or varying steam conditions






























