The following terms are used for the function described in this chapter:
● Slave-to-slave communication
● Data Exchange Broadcast (DXB.req)
● Slave-to-slave communication (is used in the following)
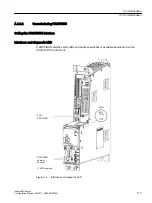
+:&RQILJ
&RQILJXUDWLRQ
5HVSRQVH
,QSXWGDWD
2XWSXWGDWD
0DVWHUFODVV
HJ6,0$7,&6
3DUDPHWHUL]DWLRQPDVWHU
3XOVHJHQHUDWRU
3*3&
6ODYH
6,1$0,&6
3XEOLVKHU
6ODYH
6,1$0,&6
6XEVFULEHU
6ODYH
6,1$0,&6
6XEVFULEHU
/LQNV
'ULYH(6%DVLF
1)
From the perspective of the Class 1 master
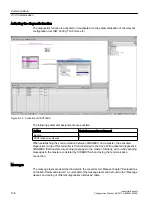
Figure A-9
Slave-to-slave communication with the publisher-subscriber model
Publisher
With the "slave-to-slave communication" function, at least one slave must act as the publisher.
The publisher is addressed by the master when the output data is transferred with a modified
layer 2 function code (DXB.req). The publisher then sends its input data for the master with a
broadcast telegram to all bus nodes.
Subscriber
The subscribers evaluate the broadcast telegrams, sent from the publishers, and use the data
which has been received as setpoints. These setpoints of the publisher are used, in addition
to the setpoints received from the master, corresponding to the configured telegram structure
(p0922).
Communication
A.1 Communication
Industrial Security
Configuration Manual, 08/2017, A5E36912609A
125