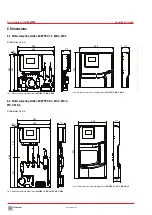
Commissioning of the water sampling station
31
Subject to technical changes.
200114
BA-42820-02-V03
Water sampling station
EASYPRO
Operating instructions
Perform the following work steps:
1.
Working in the main menu under System > Inputs, navigate to the
“Virtual” tab.
2.
Working in the “Virtual” tab, configure the desired calculation of the
bound chlorine and state the following information.
3. Calculation:
Select “bound chlorine” to calculate the bound chlorine.
4. Total chlorine:
Select the sensor which measures the total chlorine.
5. Free chlorine:
Select the sensor which measures the free chlorine. If
no sensor is present, you can enter a reference value measured once
which can be used for the calculation.
6. Min-alarm:
Activate or deactivate the minimum alarm and state a
value under which the alarm will be triggered.
7. Max-alarm:
Activate or deactivate the maximum alarm and state a
value over which the alarm will be triggered.
8. Delay:
Set a time delay for the minimum and maximum alarm.
ü
Configuration of the bound chlorine completed.
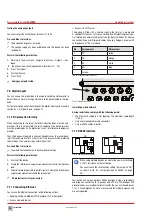
Effective chlorine
The disinfectant effect of the free chlorine is highly dependant on the pH
value of the process water. The pH value influences the reactivity of the
Chlorine ions. This relationship is underscored by the dissociation curve
(Fig. 28 „Dissociation curve of the effective chlorine“ on page 31) of
the chlorine.
The actual disinfectant effect of the chlorine is generated by the hy-
pochlorous acid (HClO). The figure shows that the proportion of the HClO
is largest between pH 2 and pH 7.5. The disinfectant effect is very low
outside this pH value.
For photometric measurements the pH value of the sample is buffered to
approx. pH 6.5. As a result the measurement has a higher effective chlo-
rine content than is actually in the process water. For high pH-values sig-
nificant differences will therefore occur between the expected and actual
disinfection if assessed by photometric analysis. The calculation of the ef-
fective chlorine can be used to display the proportion of the hypochlorous
acid (HCIO), i.e. the proportion which contributes to the disinfectant effect.
100 %
50
10
5
1
0,5
0,1
HCIO
CIO-
-..
.,,..
-----
-..
-·
'
/
"
/
X
I
\
I
\
I
\
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
1
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
1
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
I
1
1
1
0
2
4
1
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
.....
'
/
'
/
\/
�
I
\
I
\
I
\
I
\
I
\
I
\
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
6
8
1
\
\
\
\
\
\
\
\
\
\
\
1
\
\
\
\
\
\
10
12
pH > 1,7 : Cl2
+
H2O � HCIO
+
HCI
pH > 7,5 : HCIO � H
+
+
CIO-
14
(pH)
Fig. 28: Dissociation curve of the effective chlorine
Perform the following work steps:
1.
Working in the main menu under System > Inputs, navigate to the
“Virtual” tab.
2.
Working in the “Virtual” tab, configure the desired calculation of the
effective chlorine and state the following information.
3. Calculation:
Select “effective chlorine” to calculate the effective
chlorine.
4. Free chlorine:
Select the sensor which measures the free chlorine.
5. pH value:
Select the sensor which measures the pH value. If no sen-
sor is present, you can enter a reference value measured once which
can be used for the calculation.
6. Temperature:
A temperature value is required to calculate the effec-
tive chlorine. Select the temperature input which can be used for the
calculation. If no temperature sensor is present, you can set a refer-
ence value measured once which can be used for the calculation.
7. Min-alarm:
Activate or deactivate the minimum alarm and state a
value under which the alarm will be triggered.
8. Max-alarm:
Activate or deactivate the maximum alarm and state a
value over which the alarm will be triggered.
9. Delay:
Set a time delay for the minimum and maximum alarm.
ü
Configuration of the calculation of the effective chlorine
completed.