570
APPENDIX C Instruction Overview
C.3 Bit Manipulation Instructions (SETB, CLRB)
Some peripheral function registers include bits that are read differently than usual by a
bit manipulation instruction.
■
Read-modify-write Operation
By using these bit manipulation instructions, you can set only the specified bit in a register or RAM
location to "1" (SETB) or clear to "0" (CLRB). However, as the CPU operates data in 8-bit units, the actual
operation (read-modify-write operation) involves a sequence of steps: 8-bit data is read, the specified bit is
changed, and the data is written back to the location at the original address.
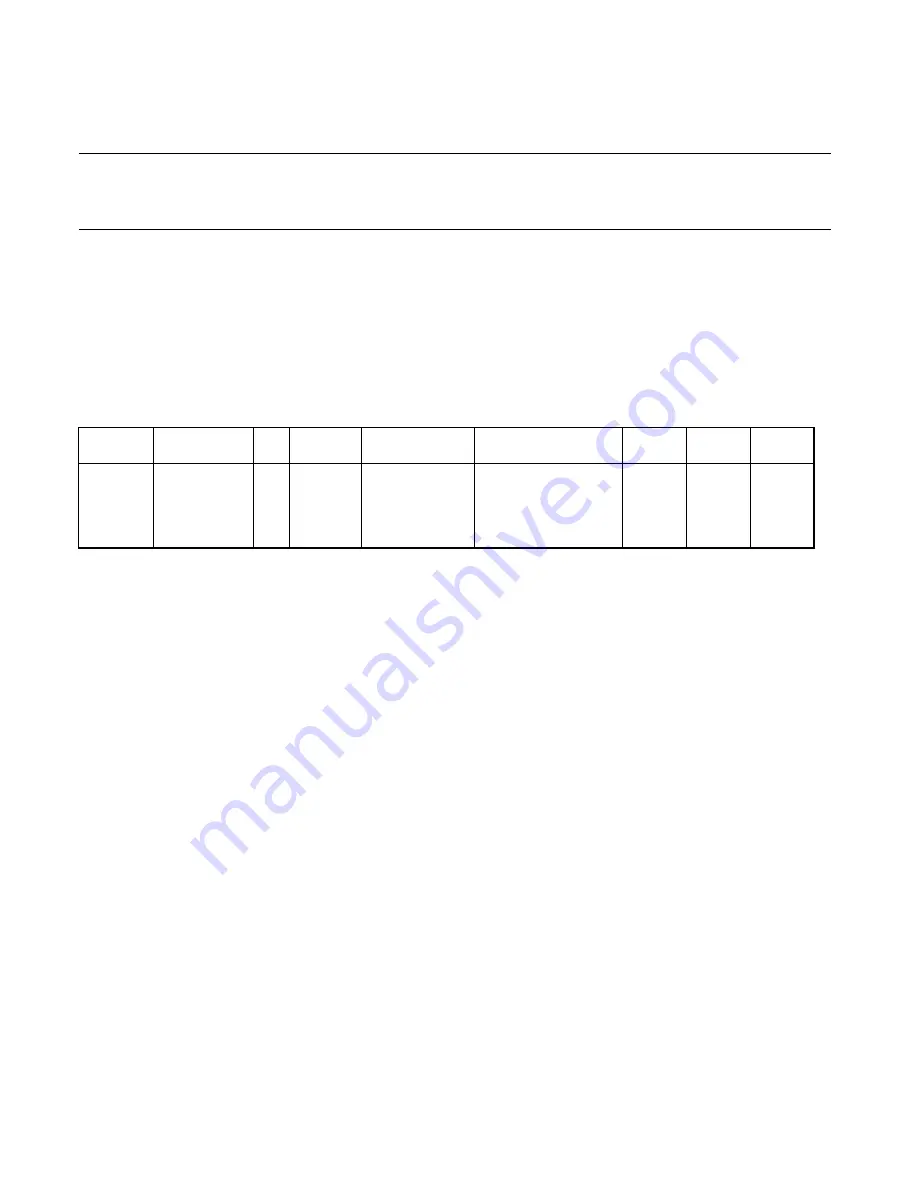
Table C.3-1 shows bus operation for bit manipulation instructions.
■
Read Destination on the Execution of Bit Manipulation Instructions
For some I/O ports and the interrupt request flag bits, the read destination differs between a normal read
operation and a read-modify-write operation.
●
I/O ports (during a bit manipulation)
From some I/O ports, an I/O pin value is read during a normal read operation, while a port data register
value is read during a bit manipulation. This prevents the other port data register bits from being changed
accidentally, regardless of the I/O directions and states of the pins.
●
Interrupt request flag bits (during a bit manipulation)
An interrupt request flag bit functions as a flag bit indicating whether an interrupt request exists during a
normal read operation, however, "1" is always read from this bit during a bit manipulation. This prevents
the flag from being cleared accidentally by writing the value "0" to the interrupt request flag bit when
manipulating another bit.
Table C.3-1 Bus Operation for Bit Manipulation Instructions
CODE
MNEMONIC
~
Cycle
Address bus
Data bus
RD
WR
RMW
A0 to A7
A8 to AF
CLRB dir:b
SETB dir:b
4
1
2
3
4
N+2
dir address
dir address
N+3
Next instruction
Data
Data
Instruction after next
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
Summary of Contents for F2 MC-8FX Family
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 34: ...20 CHAPTER 1 DESCRIPTION ...
Page 38: ...24 CHAPTER 2 HANDLING DEVICES ...
Page 39: ...25 CHAPTER 3 MEMORY SPACE This chapter describes memory space 3 1 Memory Space 3 2 Memory Map ...
Page 56: ...42 CHAPTER 5 CPU ...
Page 73: ...59 CHAPTER 6 CLOCK CONTROLLER ...
Page 96: ...82 CHAPTER 6 CLOCK CONTROLLER ...
Page 104: ...90 CHAPTER 7 RESET ...
Page 105: ...91 CHAPTER 8 INTERRUPTS This chapter explains the interrupts 8 1 Interrupts ...
Page 174: ...160 CHAPTER 10 TIMEBASE TIMER ...
Page 184: ...170 CHAPTER 10 TIMEBASE TIMER ...
Page 218: ...204 CHAPTER 13 WATCH PRESCALER ...
Page 257: ...243 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 261: ...247 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 288: ...274 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 301: ...287 CHAPTER 17 16 BIT PPG TIMER ...
Page 316: ...302 CHAPTER 17 16 BIT PPG TIMER ...
Page 382: ...368 CHAPTER 21 UART SIO DEDICATED BAUD RATE GENERATOR ...
Page 390: ...376 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 395: ...381 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 399: ...385 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 430: ...416 CHAPTER 23 10 BIT A D CONVERTER ...
Page 476: ...462 CHAPTER 24 LCD CONTROLLER ...
Page 482: ...468 CHAPTER 25 LOW VOLTAGE DETECTION RESET CIRCUIT ...
Page 494: ...480 CHAPTER 26 CLOCK SUPERVISOR ...
Page 507: ...493 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 523: ...509 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 532: ...518 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 536: ...522 CHAPTER 28 256 KBIT FLASH MEMORY ...
Page 554: ...540 CHAPTER 28 256 KBIT FLASH MEMORY ...
Page 564: ...550 CHAPTER 29 EXAMPLE OF SERIAL PROGRAMMING CONNECTION ...
Page 595: ...581 INDEX INDEX The index follows on the next page This is listed in alphabetic order ...
Page 596: ...582 INDEX Index ...
Page 597: ...583 INDEX ...
Page 600: ...586 Pin Function Index ...
Page 602: ......
















































