403
CHAPTER 22 I
2
C
22.7.2
Function to Wake up the MCU from Standby Mode
The wakeup function enables the I
2
C macro to be accessed while the MCU is in stop or
watch mode.
■
Function to Wake Up the MCU from Standby Mode
The I
2
C macro includes a function to wake up the MCU from standby mode. The function is enabled by
writing "1" to the IBCR00:WUE bit.
When the MCU is in stop/watch mode with the IBCR00:WUE bit containing "1", if a start condition is
detected on the I
2
C bus, the wakeup interrupt request flag bit (IBCR00:WUF) is set to "1" and the wakeup
interrupt request is generated to wake up the MCU from stop/watch mode.
•
Set IBCR00:WUE to "1" immediately prior to setting the MCU to stop or watch mode. Similarly, clear
IBCR00:WUE (by writing "0") after the MCU wakes up from stop or watch mode so that I
2
C operation
can restart as soon as possible.
•
The wakeup function only applies to the MCU stop and watch modes.
Note:
In PLL stop mode, a PLL oscillation stabilization wait time is required in addition to the oscillation
stabilization wait time. This causes a very long delay between the MCU waking up and
communications restarting.
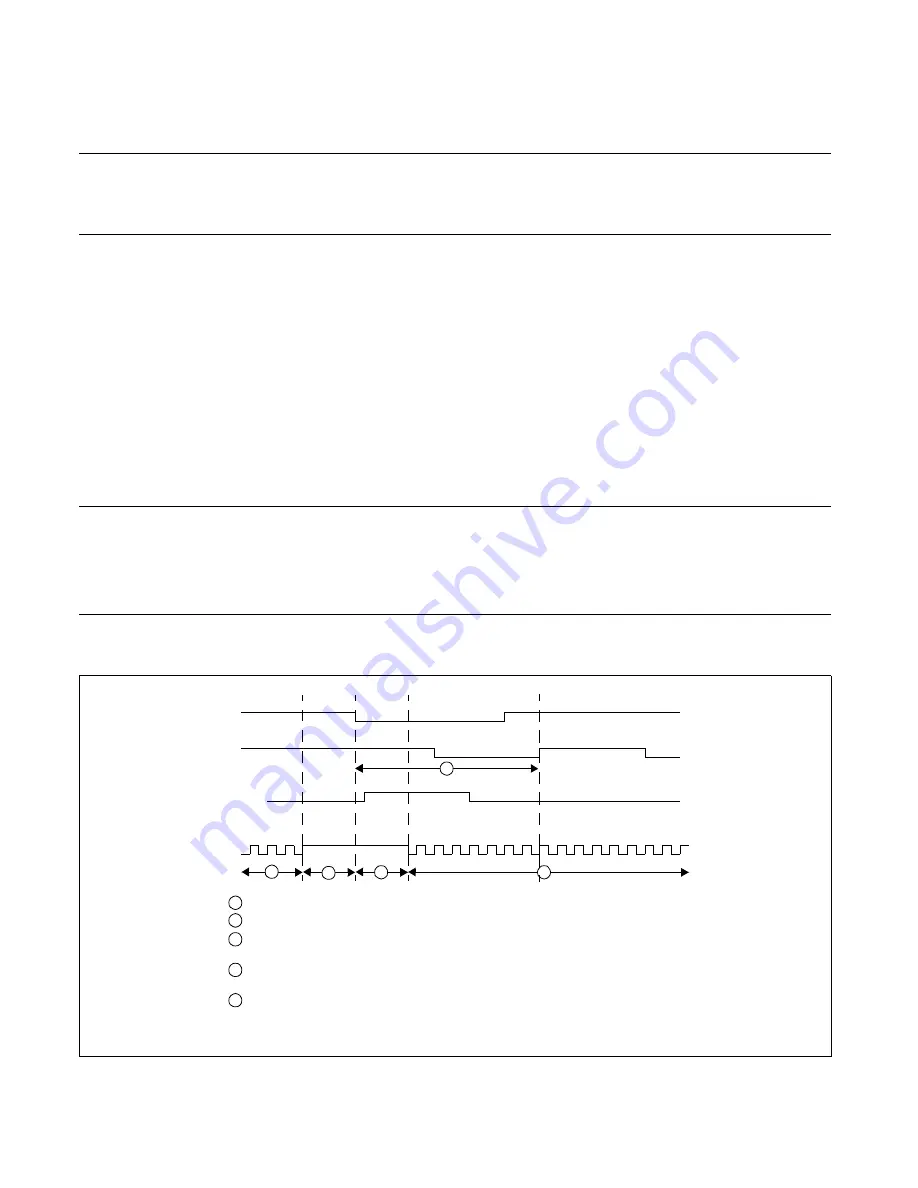
Figure 22.7-7 Comparison of Normal I
2
C Operation and Wakeup Operation
SDA0
SCL0
IRQ by
IBCR00:WUF
Machine
Clock
1
2
3
4
5
1
Set the IBCR00:WUE bit to "1" immediately before entering stop/watch mode and make sure that IBSR0:BB = 0.
2
Set the MCU to stop/watch mode and the machine clock stops.
3
Detect a start condition in stop/watch mode. IBCR00:WUF is set to 1 and a wakeup IRQ is generated. After the
oscillation stabilization wait time, the MCU wakes up and enters main clock mode.
4
Clear the IBCR00:WUE bit to "0" so that I
2
C can restart the normal operation, and clear the IBCR00:WUF bit to
"0" to clear the wakeup interrupt.
5
To receive the data byte correctly, the SCL0 must be released in the first cycle after 100
μ
s (assuming a
minimum oscillation stabilization wait time of 100
μ
s) from the start of I
2
C transmission (falling edge detection of
SDA0).
Summary of Contents for F2 MC-8FX Family
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 34: ...20 CHAPTER 1 DESCRIPTION ...
Page 38: ...24 CHAPTER 2 HANDLING DEVICES ...
Page 39: ...25 CHAPTER 3 MEMORY SPACE This chapter describes memory space 3 1 Memory Space 3 2 Memory Map ...
Page 56: ...42 CHAPTER 5 CPU ...
Page 73: ...59 CHAPTER 6 CLOCK CONTROLLER ...
Page 96: ...82 CHAPTER 6 CLOCK CONTROLLER ...
Page 104: ...90 CHAPTER 7 RESET ...
Page 105: ...91 CHAPTER 8 INTERRUPTS This chapter explains the interrupts 8 1 Interrupts ...
Page 174: ...160 CHAPTER 10 TIMEBASE TIMER ...
Page 184: ...170 CHAPTER 10 TIMEBASE TIMER ...
Page 218: ...204 CHAPTER 13 WATCH PRESCALER ...
Page 257: ...243 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 261: ...247 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 288: ...274 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 301: ...287 CHAPTER 17 16 BIT PPG TIMER ...
Page 316: ...302 CHAPTER 17 16 BIT PPG TIMER ...
Page 382: ...368 CHAPTER 21 UART SIO DEDICATED BAUD RATE GENERATOR ...
Page 390: ...376 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 395: ...381 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 399: ...385 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 430: ...416 CHAPTER 23 10 BIT A D CONVERTER ...
Page 476: ...462 CHAPTER 24 LCD CONTROLLER ...
Page 482: ...468 CHAPTER 25 LOW VOLTAGE DETECTION RESET CIRCUIT ...
Page 494: ...480 CHAPTER 26 CLOCK SUPERVISOR ...
Page 507: ...493 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 523: ...509 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 532: ...518 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 536: ...522 CHAPTER 28 256 KBIT FLASH MEMORY ...
Page 554: ...540 CHAPTER 28 256 KBIT FLASH MEMORY ...
Page 564: ...550 CHAPTER 29 EXAMPLE OF SERIAL PROGRAMMING CONNECTION ...
Page 595: ...581 INDEX INDEX The index follows on the next page This is listed in alphabetic order ...
Page 596: ...582 INDEX Index ...
Page 597: ...583 INDEX ...
Page 600: ...586 Pin Function Index ...
Page 602: ......















































