384
CHAPTER 22 I
2
C
Note:
•
When clearing the interrupt request flag (IBCR10:BER) by writing "0", do not update the
interrupt request enable bit (IBCR10:BEIE) at the same time.
•
All the bits in IBCR10 except the BER and BEIE bits are cleared to "0" either when operation is
disabled (ICCR:EN = 0) or when a bus error occurs (IBSR0:BER = 1).
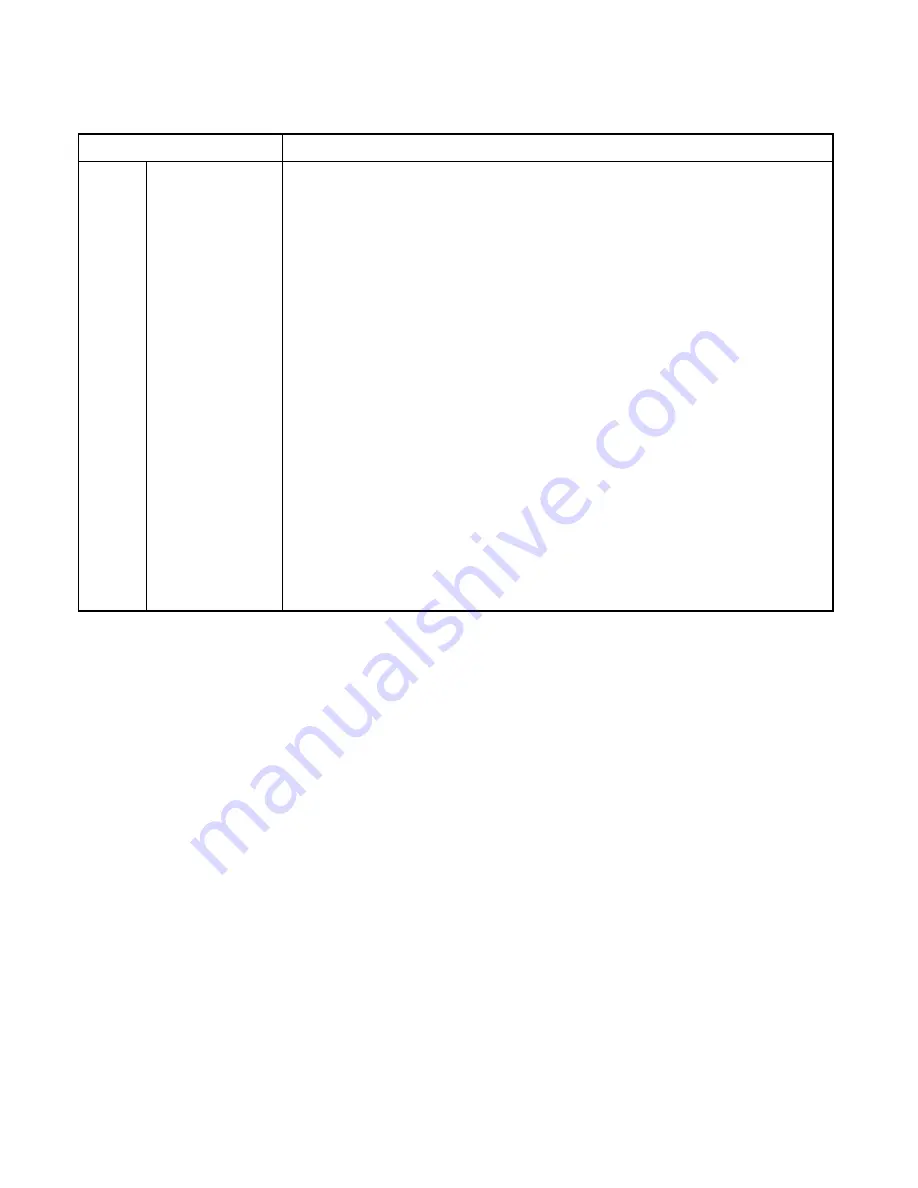
bit0
INT:
Transfer completion
interrupt request flag
bit
This bit is used to detect transfer completion.
• A transfer completion interrupt request is generated if this bit and the IBCR10:INTE bit are both
"1".
• This bit is set to "1" upon completion of transfer of 1-byte address or data (whether or not this
includes an acknowledgment depends on the IBCR00:INTS setting) if any of the following four
conditions is satisfied.
- In bus master mode
- Addressed as slave
- General call address received
- Arbitration lost detected
• This bit is set to "0" in the following cases:
- "0" written to the bit
- Repeated start condition (IBCR10:SCC = 1) or stop condition (IBCR10:MSS = 0) occurred in
master mode.
• An attempt to write "1" to this bit leaves its value unchanged and has no effect on the operation.
• The bit returns "1" when read by a read-modify-write operation.
• The SCL0 line remains at "L" while this bit is "1".
• Writing "0" to clear the bit (change the value to "0") releases the SCL0 line to enable transmission
for the next byte of data.
Note:
• If "1" is written to IBCR10:SCC when this bit is "0", the IBCR10:SCC bit has priority
and the start condition is generated.
• If "0" is written to IBCR10:MSS when this bit is "0", the IBCR10:MSS bit has priority
and the stop condition is generated.
• If IBCR00:INTS = 1 when data is received, this bit is set to "1" upon completion of
transfer of one-byte data (including no acknowledgment). In other cases, this bit is set to
"1" upon completion of transmission or reception of one-byte data/address including an
acknowledgment.
Table 22.5-2 I
2
C Bus Control Register 1 (IBCR10) (2 / 2)
Bit name
Function
Summary of Contents for F2 MC-8FX Family
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 34: ...20 CHAPTER 1 DESCRIPTION ...
Page 38: ...24 CHAPTER 2 HANDLING DEVICES ...
Page 39: ...25 CHAPTER 3 MEMORY SPACE This chapter describes memory space 3 1 Memory Space 3 2 Memory Map ...
Page 56: ...42 CHAPTER 5 CPU ...
Page 73: ...59 CHAPTER 6 CLOCK CONTROLLER ...
Page 96: ...82 CHAPTER 6 CLOCK CONTROLLER ...
Page 104: ...90 CHAPTER 7 RESET ...
Page 105: ...91 CHAPTER 8 INTERRUPTS This chapter explains the interrupts 8 1 Interrupts ...
Page 174: ...160 CHAPTER 10 TIMEBASE TIMER ...
Page 184: ...170 CHAPTER 10 TIMEBASE TIMER ...
Page 218: ...204 CHAPTER 13 WATCH PRESCALER ...
Page 257: ...243 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 261: ...247 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 288: ...274 CHAPTER 16 8 16 BIT COMPOSITE TIMER ...
Page 301: ...287 CHAPTER 17 16 BIT PPG TIMER ...
Page 316: ...302 CHAPTER 17 16 BIT PPG TIMER ...
Page 382: ...368 CHAPTER 21 UART SIO DEDICATED BAUD RATE GENERATOR ...
Page 390: ...376 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 395: ...381 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 399: ...385 CHAPTER 22 I2C ...
Page 430: ...416 CHAPTER 23 10 BIT A D CONVERTER ...
Page 476: ...462 CHAPTER 24 LCD CONTROLLER ...
Page 482: ...468 CHAPTER 25 LOW VOLTAGE DETECTION RESET CIRCUIT ...
Page 494: ...480 CHAPTER 26 CLOCK SUPERVISOR ...
Page 507: ...493 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 523: ...509 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 532: ...518 CHAPTER 27 REAL TIME CLOCK ...
Page 536: ...522 CHAPTER 28 256 KBIT FLASH MEMORY ...
Page 554: ...540 CHAPTER 28 256 KBIT FLASH MEMORY ...
Page 564: ...550 CHAPTER 29 EXAMPLE OF SERIAL PROGRAMMING CONNECTION ...
Page 595: ...581 INDEX INDEX The index follows on the next page This is listed in alphabetic order ...
Page 596: ...582 INDEX Index ...
Page 597: ...583 INDEX ...
Page 600: ...586 Pin Function Index ...
Page 602: ......















































