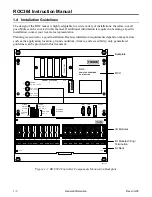
ROC364 Instruction Manual
1-6
General Information
Rev Jun/05
Proper grounding of the ROC helps to reduce the effects of electrical noise on unit operation and helps
protect against lightning. Lightning Protection Modules are available to provide additional lightning
protection for field wiring inputs and outputs. Refer to Appendix A for information about lightning
protection. A surge protection device installed at the service disconnect on line-powered systems also
offers lightning and power surge protection for the installed equipment.
Telephone surge protectors should be installed for ROC units using modem communications cards.
All earth grounds must have an earth-to-ground rod or grid impedance of 25 ohms or less as measured
with a ground system tester. The grounding conductor should have a resistance of 1 ohm or less between
the ROC enclosure ground lug and the earth ground rod or grid.
1.4.6 I/O Wiring Requirements
I/O wiring requirements are site and application dependent. Local, state, and NEC requirements
determine the I/O wiring installation methods. Direct buried cable, conduit and cable, or overhead
cable are options for I/O wiring installations. Refer to Section 2, Master Controller Unit, I/O Module
Rack, and Wiring, and Section 3, Input/Output Modules.
1.5 Power Supply Requirements
The power consumption of a ROC and related devices determines the requirements for either line
or solar power supplies. Table 1-1 and Table 1-2 provide information to assist in determining power
supply requirements.
Table 1-1 lists the power consumption of the ROC364 and the optional devices available for it. Include
in the power consumption calculations of all device relays, meters, solenoids, radios, and other devices
that receive DC power from the ROC (excluding those connected to the I/O modules). Table 1-2 lists the
power consumption of the various I/O modules available.
A ROC systems power consumption determines power supply and battery size for both line and solar
power supplies. Use the information in Table 1-1 and Table 1-2 to determine power requirements.
For non-analog I/O, size the I/O module scaling resistors for optimal current to minimize current drain
on the power supply. Refer to Section 3.
1.5.1 Determining I/O Channel Power Consumption
To determine the I/O Channel Power:
1.
Calculate the
Duty Cycle
of each I/O channel and enter the values in Table 1-1.
In estimating total I/O power requirements, the Duty Cycle of each I/O channel (built-in I/O or
modular I/O) must be estimated.
For a non-analog I/O channel
, the Duty Cycle is the percentage of time that the I/O channel is
active (maximum power consumption). For example, if a Discrete Output is active for 15
seconds out of every 60 seconds, the Duty Cycle is:
Duty Cycle = Active time
÷
(Active time + Inactive time) = 15 sec
÷
60 sec = 0.25
NOTE:
For non-analog I/O, size the I/O module scaling resistors for optimal current to
minimize current drain on the power supply.