TCP/IP Example Settings
Basic TCP/IP settings
A-2
Preliminary January 30, 1998
Pipeline Start Here Guide
Basic TCP/IP settings
When setting up TCP/IP, you need an IP address for your Pipeline and for each
computer on your network. The main concern for most users is where to get the
IP addresses, since most Internet Service Providers and many corporate network
administrators assign you a single IP address when you logon to their network.
The following example shows you how to set up private addresses on your local
network and obtain an IP address dynamically when logging onto the Internet or
your corporate LAN.
The table below shows sample values that you can use for a private network if
you are not assigned a set of IP addresses.
Note:
If you are assigned unique IP addresses, be sure to use the lowest number
for the Pipeline, since it is the gateway on your network.
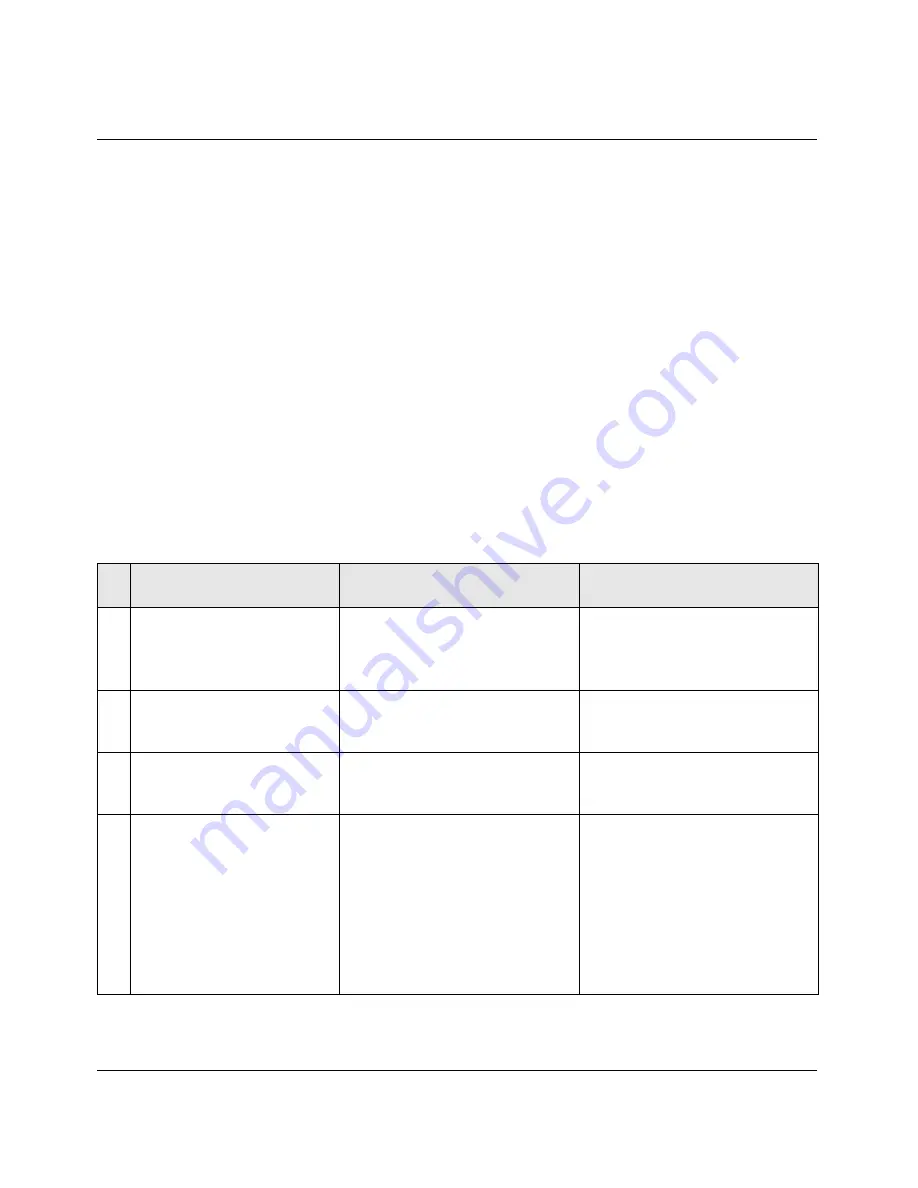
Table A -1.A numbered list of sample TCP/IP values
#
Name/Address
Sample values
Comments
1
IP address for Pipeline
(the router or default
gateway)
192.168.100.1
Standard private IP addresses
start at 192.168.xxx.xxx
2
IP address of computer
(also know as a host)
192.168.100.2
Use the next address after the
address of the Pipeline.
3
Subnet address (or subnet
mask) of your network
255.255.255.0 or /24
This is the standard subnet
address for a Class C host.
4
Host name and domain
(the host name is required
for PC settings only)
If you weren’t assigned a host
name, use any name, such as:
host-2. (Don’t enter your
account logon name here.)
Your domain is what follows
the @ sign in your email
address, as in: bignet.com
If you were assigned an IP
address for your computer
and your Pipeline, you might
also have been assigned
corresponding names, in
which case, use the assigned
host name.






























