Indirect Addressing Mode
6-13
Addressing Modes
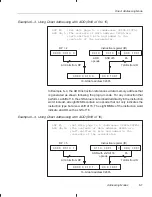
Table 6–2. Effects of the ARU Code on the Current Auxiliary Register
ARU Code
6
5
4
Arithmetic Operation Performed on Current AR
0
0
0
No operation on current AR
0
0
1
current AR – 1
→
current AR
0
1
0
current AR + 1
→
current AR
0
1
1
Reserved
1
0
0
current AR – AR0
→
current AR [reverse carry propagation]
1
0
1
current AR – AR0
→
current AR
1
1
0
current AR + AR0
→
current AR
1
1
1
current AR + AR0
→
current AR [reverse carry propagation]
N
Next auxiliary register indicator. Bit 3 specifies whether the
instruction will change the ARP value.
N = 0
If N is 0, the content of the ARP will remain un-
changed.
N = 1
If N is 1, the content of NAR will be loaded into
the ARP, and the old ARP value is loaded into
the auxiliary register buffer (ARB) of status reg-
ister ST1.
NAR
Next auxiliary register value. Bits 2 through 0 contain the
value of the next auxiliary register. NAR is loaded into the ARP
if N = 1.
Table 6–3 shows the opcode field bits and the notation used for indirect ad-
dressing. It also shows the corresponding operations performed on the current
auxiliary register and the ARP.