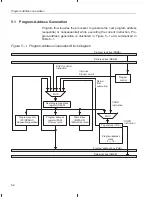
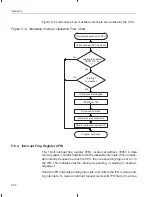
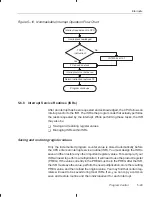
Repeating a Single Instruction
5-14
5.5
Repeating a Single Instruction
The ’C2xx repeat (RPT) instruction allows the execution of a single instruction
N + 1 times, where N is specified as an operand of the RPT instruction. When
RPT is executed, the repeat counter (RPTC) is loaded with N. RPTC is then
decremented every time the repeated instruction is executed, until RPTC
equals zero. RPTC can be used as a 16-bit counter when the count value is
read from a data-memory location; if the count value is specified as a constant
operand, it is in an 8-bit counter.
The repeat feature is useful with instructions such as NORM (normalize con-
tents of accumulator), MACD (multiply and accumulate with data move), and
SUBC (conditional subtract). When instructions are repeated, the address and
data buses for program memory are free to fetch a second operand in parallel
with the address and data buses for data memory. This allows instructions
such as MACD and BLPD to effectively execute in a single cycle when re-
peated.