Receiver Operation
9-25
Synchronous Serial Port
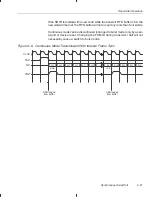
If a frame sync pulse occurs during reception, reception is restarted, and the
bits that were shifted into the RSR before the pulse are lost.
Figure 9–8. Burst Mode Reception
CLKR
FSR
DR
RINT
A15
MSB
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
...
A0
B15
LSB
Word loaded
to buffer
from RSR
B14
MSB
9.6.2
Continuous Mode Reception
Use continuous mode receive to transfer long packets at maximum packet fre-
quency.
This mode of operation offers several features:
-
Only the first frame sync signal is necessary to start the reception of con-
secutive words.
-
As long as the receive FIFO buffer is not allowed to overflow, the mode
continues. Overflow is indicated by the OVF bit in the SSPCR.
-
Reception can be maintained continuously.
Generally, the transmit clock and the receive clock have the same source. This
allows each bit to be transmitted from another device on a rising edge of the
clock signal and received by the ’C2xx on the next falling edge of the clock sig-
nal.
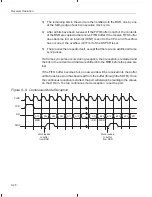
As shown in Figure 9–9, the following events occur during a continuous mode
receive operation:
1) The receive operation begins when a frame sync signal is detected on the
falling edge of CLKR.
2) On the first falling edge of CLKR after the frame sync signal goes low, the
first bit (MSB) is shifted into the RSR.