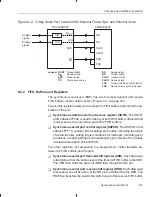
Transmitter Operation
9-16
9.5
Transmitter Operation
Transmitter operation is different in continuous and burst modes. Other differ-
ences also depend on whether an internal or an external frame sync is used.
9.5.1
Burst Mode Transmission With Internal Frame Sync (FSM = 1, TXM = 1)
Use burst mode transmission with internal frame sync to transfer short packets
at rates lower than maximum packet frequency while using an internal frame
sync generator. Place the transmitter in burst mode with internal frame sync
by setting the FSM bit to 1 and the TXM bit to 1.
This mode of operation offers several features:
-
A one-clock-cycle frame-sync pulse is generated internally at the begin-
ning of each transmission.
-
Continuous transmission is possible if SDTR is updated in the XINT inter-
rupt service routine.
-
Transmission can be initiated by an external event (for example, an exter-
nal interrupt) or by a receive interrupt (RINT).
Generally, the transmit clock and the receive clock have the same source. This
allows each bit to be transmitted from another device on a rising edge of the
clock signal and received by the ’C2xx on the next falling edge of the clock sig-
nal.
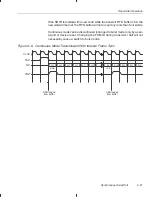
Burst mode transmission with internal frame sync requires the following order
of events (see Figure 9–4 ):
1) Initiate the transfer by writing to SDTR.
2) A frame sync pulse is generated on the next rising edge of CLKX. The
frame sync pulse remains high for one clock cycle.
3) On the next rising edge of CLKX after FSX goes high, XSR is loaded with
the value at the bottom of the FIFO buffer, and the frame sync pulse goes
low. Additionally, the first data bit (MSB first) is driven on the DX pin. If the
FIFO buffer becomes empty during this operation, then it generates XINT
to request more data.
4) The rest of the bits are then shifted out. Each new bit is transmitted at each
consecutive rising edge of CLKX.
5) If the FIFO buffer still holds a word or words to be transmitted, another
frame sync pulse is generated in parallel to the driving of the LSB on the
DX pin, and transmission continues at step 3. If the FIFO is empty, trans-
mission is complete.