SAR
Store Auxiliary Register
7-152
Syntax
SAR AR
x, dma
Direct addressing
SAR AR
x, ind [, ARn]
Indirect addressing
Operands
dma:
7 LSBs of the data-memory address
x:
Value from 0 to 7 designating the auxiliary register value to be
stored
n:
Value from 0 to 7 designating the next auxiliary register
ind:
Select one of the following seven options:
* *+ *– *0+ *0– *BR0+ *BR0–
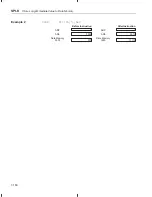
SAR AR
x, dma
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
x
0
dma
SAR AR
x, ind [, ARn]
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
x
0
ARU
N
NAR
Note:
ARU, N, and NAR are defined in Section 6.3,
Indirect Addressing Mode (page 6-9).
Execution
Increment PC, then ...
(ARx)
→
data-memory address
Status Bits
None
Description
The content of the designated auxiliary register (ARx) is stored in the specified
data-memory location. When the content of the designated auxiliary register
is also modified by the instruction (in indirect addressing mode), SAR copies
the auxiliary register value to data memory before it increments or decrements
the contents of the auxiliary register.
Words
1
Cycles for a Single SAR Instruction
Program
Operand
ROM
DARAM
SARAM
External
DARAM
1
1
1
1+p
SARAM
1
1
1, 2
†
1+p
External
2+d
2+d
2+d
4+d+p
† If the operand and the code are in the same SARAM block
Opcode
Cycles