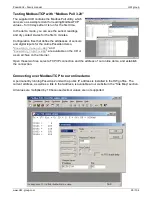
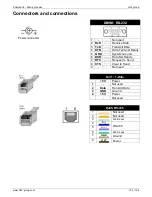
Poseidon2
– Family manual
HW group
www.HW-group.com
101 / 104
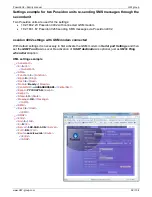
SNMP Trap
– Interface description
Whenever a value gets outside of the safe range for a
sensor, the sensor enters the ALARM state. To notify
about the alarm state, a SNMP trap is send to the
specified IP address.
SNMP traps consist of
two UDP packets
sent by the
SNMP Agent to the monitoring center (SNMP Client).
The packet format is detailed in the MIB table. The first
packet contains information about raising the ALARM, the second packet contains additional info
about the sensor causing the alarm. When the alarm state ends (e.g. the temperature returns to the
safe range), two more UDP packets are sent to inform about the termination of the alarm state.
This method was developed for faster notification of alarms because
– in the normal request /
response SNMP mode
– the polling period may range from hundreds of milliseconds to minutes or
even days.
For dry contacts, alarm can be sent upon opening/closing, or turned off completely.
SNMP traps sent by the Poseidon
The MIB table contains a list as well as detailed descriptions of SNMP traps. An overview follows.
Cold Start + Link Up Trap
A pair of SNMP traps sent after the device starts up. If a sensor is in alarm upon startup, two
more traps immediately follow.
Alarm raised on a dry contact
A pair of SNMP traps sent when an alarm is activated for a dry contact. The first trap
contains alarm activation identification for maintaining the “alarm table”. The second trap
contains, for instance, the name of the input in alarm.
Alarm terminated on a dry contact
A pair of SNMP traps sent when an alarm ends for a dry contact. This pair is always
preceded by the traps related to the alarm activation. The first trap contains alarm activation
identification for maintaining the “alarm table”. The second trap contains, for instance, the
name of the input in alarm.
Alarm activated due to sensor value
A pair of SNMP traps sent when a sensor alarm is activated (temperature, humidity and
others). Alarm is activated if the reading gets out of the defined range
hysteresis. The first
trap contains alarm activation identification for maintaini
ng the “alarm table”. The second trap
contains the assigned sensor name and the value causing the alarm.
Alarm activated due to sensor value
A pair of SNMP traps sent when a sensor alarm is activated (temperature, humidity and
others). Alarm ends when the reading returns back to the safe range
hysteresis. The first
trap contains alarm activation identification for maintaining the “alarm table”. The second trap
contains the assigned sensor name and the value causing the alarm.