Cryo-con Model 24C
Specifications, Features and Functions
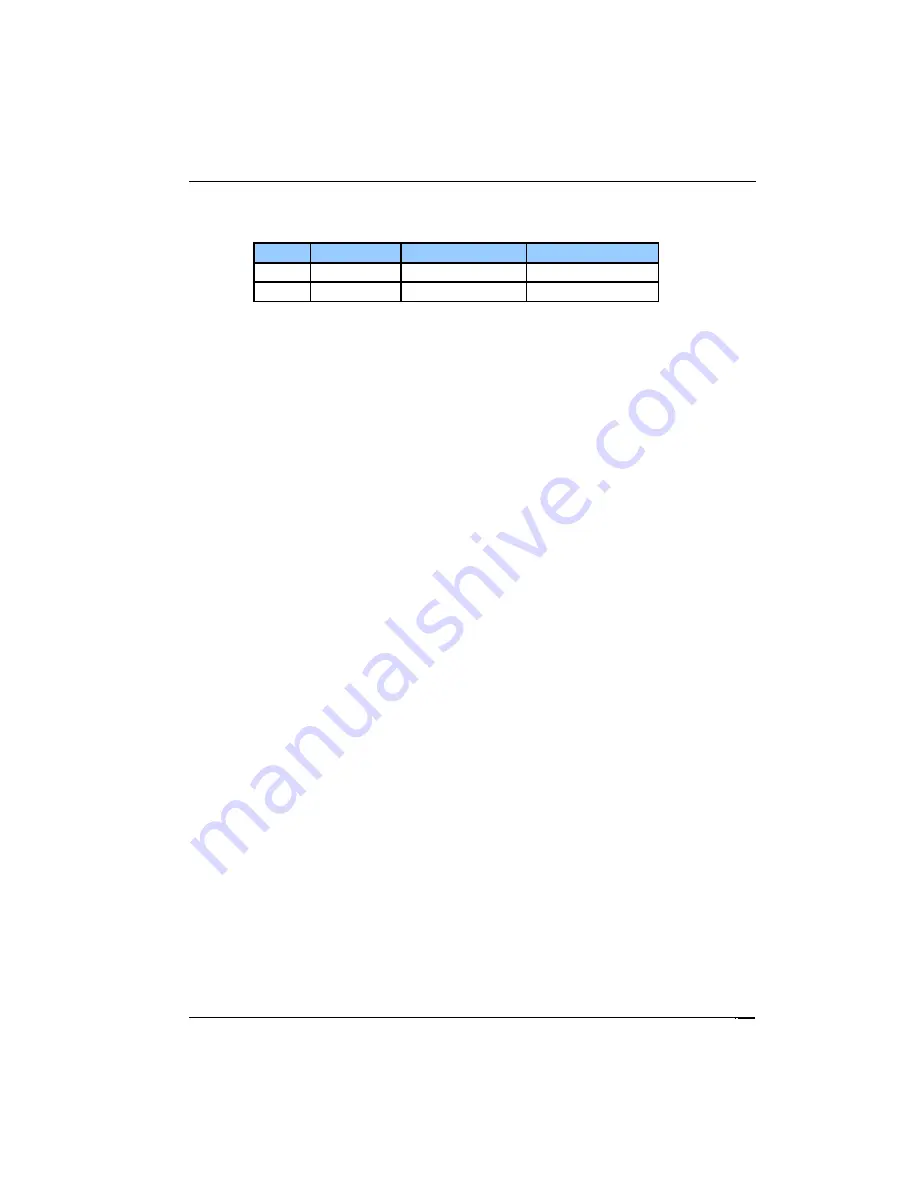
Control Loop #2, Secondary Heater Output
Control loop #2 is a constant current source similar to Loop #1.
Range
Compliance
Full-Scale Current
Max. Output Power
High
36V
0.71A
25 Watts
Low
36V
0.22A
2.5 Watts
Table 13: Loop 2 Heater output ranges.
Control Types
There are four control types available in the Model 24C. They are Manual, PID, PID
Table, Ramp and Ramp Table. All modes are available on all control loops.
Manual mode operation allows setting the output power manually as a percentage of
full-scale power.
PID control allows feedback control using an enhanced PID algorithm that is
implemented using 32-bit floating point Digital Signal Processing techniques.
Enhancements include:
1. Noise filtering on the derivative term. The D term will provide better
control stability, but is often not used because, without filtering, it makes
the control loop too sensitive to noise.
2. Integrator wind up compensation. While slewing to a new setpoint, the
integrator in the PID loop can build up to a very large value. If no
compensation is applied, overshoot and time to stability at the new
setpoint can be delayed for an extremely long time. This is especially true
in cryogenic environments where process time constants can be very
long.
3. Dithering and filtering the outputs in order to increase output resolution
and improve control stability.
The PID Table control mode is a PID control loop just as described above. However, it
is used to look up PID and heater range values based on the specified setpoint. This
is useful where a process must operate over a wide range temperature range since
optimum PID values usually change with temperature.
To use the Table mode effectively, the user must first characterize the cryogenic
process over the range of temperature that will be used, then generate PID and
heater range values for various temperature zones. This is usually done using the
autotune capability. Once the information is placed into a PID Table, the Model 24C
will control in Table mode by interpolating optimum PID values based on setpoint.
The Model 24C allows for the entry of six independent PID Tables. Each table may
contain up to 16 temperature zones.
In the Ramp control mode, the controller approaches a new setpoint at a user
specified rate. When this setpoint is reached, the controller will revert to PID control.
35






























