GR716-DS-UM, May 2019, Version 1.29
212
www.cobham.com/gaisler
GR716
25.1
Overview
The CAN controller is assumed to operate in an AMBA bus system where both the AMBA AHB bus
and the APB bus are present. The AMBA APB bus is used for configuration, control and status han-
dling. The AMBA AHB bus is used for retrieving and storing CAN messages in memory external to
the CAN controller. This memory can be located on-chip, as shown in the block diagram, or external
to the chip.
The CAN controller supports transmission and reception of sets of messages by use of circular buffers
located in memory external to the core. Separate transmit and receive buffers are assumed. Reception
and transmission of sets of messages can be ongoing simultaneously.
After a set of message transfers has been set up via the AMBA APB interface the DMA controller ini-
tiates a burst of read accesses on the AMBA AHB bus to fetch messages from memory, which are per-
formed by the AHB master. The messages are then transmitted by the CAN core. When a
programmable number of messages have been transmitted, the DMA controller issues an interrupt.
After the reception has been set up via the AMBA APB interface, messages are received by the CAN
core. To store messages to memory, the DMA controller initiates a burst of write accesses on the
AMBA AHB bus, which are performed by the AHB master. When a programmable number of mes-
sages have been received, the DMA controller issues an interrupt.
The CAN controller can detect a SYNC message and generate an interrupt, which is also available as
an output signal from the core. The SYNC message identifier is programmable via the AMBA APB
interface. Separate synchronisation message interrupts are provided.
The CAN controller can transmit and receive messages on either of two CAN busses, but only on one
at a time. The selection is programmable via the AMBA APB interface.
Note that it is not possible to receive a CAN message while transmitting one.
25.1.1 Function
The core implements the following functions:
•
CAN protocol
•
Message transmission
•
Message filtering and reception
•
SYNC message reception
•
Status and monitoring
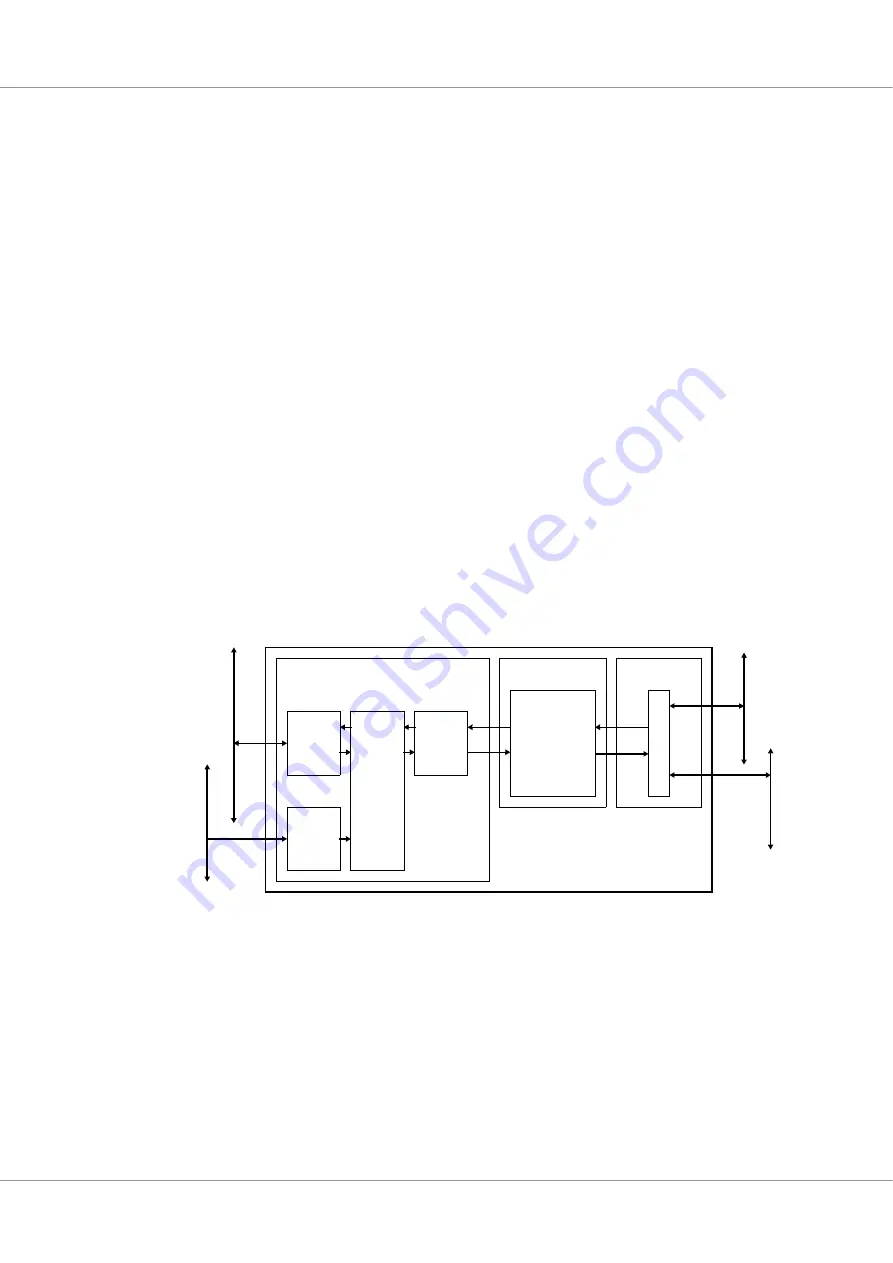
Figure 37.
Block diagram
GRCAN
DMA
AMBA
APB
Slave
AMBA Layer
Mux
/ DeMux
Coding Layer
FIFO
AMBA
AHB
Master
AMBA
AP
B
Nominal
CAN
bus
AMBA
AHB
Physical Layer
Red
unda
nt CAN bus
CAN 2.0
Codec
Controller






























