AvL Proprietary and Confidential
Content is Subject to Change without Notice
Page
96
of
195
One means of using the ref sat process is to use DBS (Direct Broadcast) satellites. They have
broad, high power carriers in the high band section of their transmitted signal. The spacing of
these satellites (in CONUS) makes it very unlikely that an adjacent satellite will be acquired.
DBS type satellites are often used as their high carrier power simplifies acquisition in poor
weather conditions as well.
In the following example our Target satellite is AMC-9 @ 83 degrees west and uses RSL for
acquisition. For our location, this satellite is near the top of the geostationary arc, which is
prone to greater pointing error. The DBS satellite Echostar-3 is at 61.5 degrees west, which is
more than 20 degrees further east and considerably lower on the arc which makes it a good
candidate for our reference. Other CONUS DBS examples are 101W, 110W & 119W.
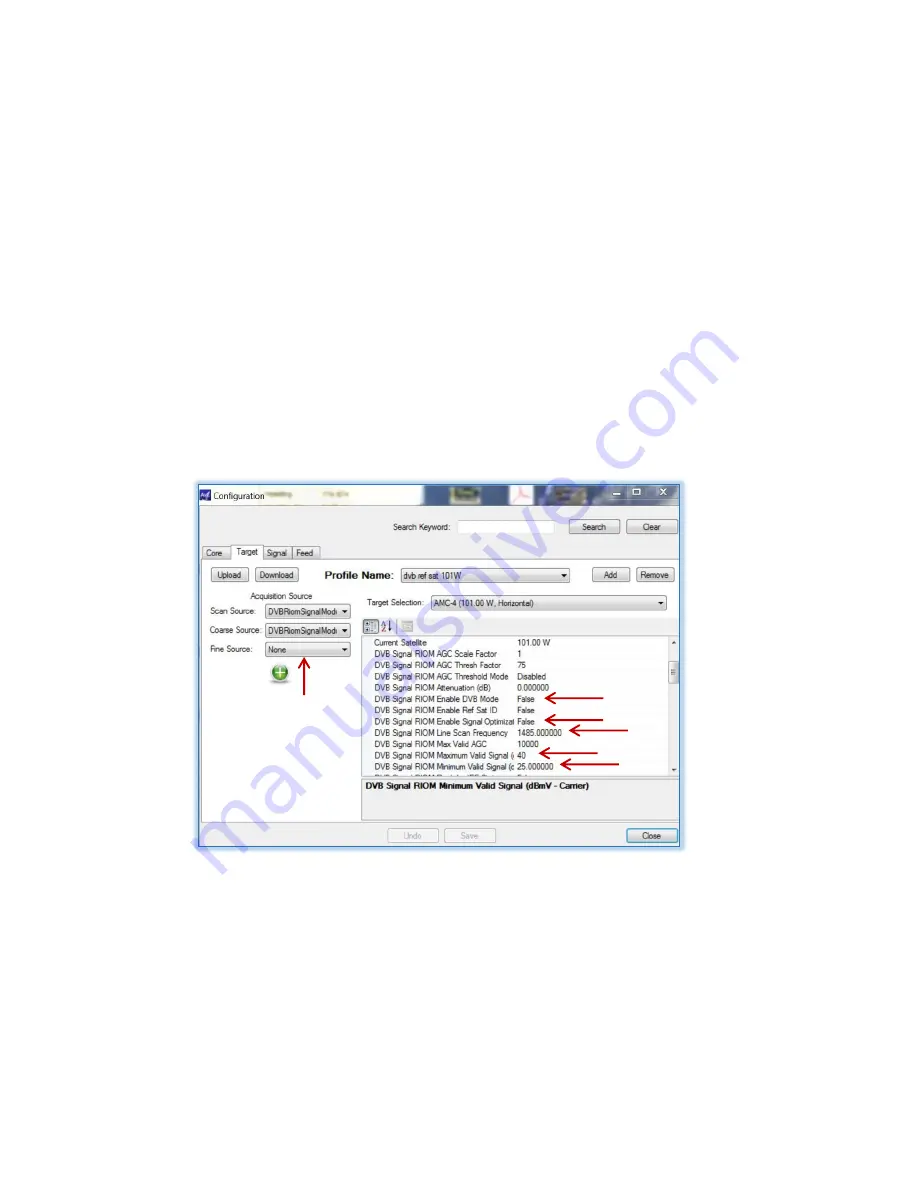
5.10.1 Create a Reference Profile
When a profile is created for the Reference satellite, it can be then selected as the “reference”
for our Target satellite. As this Reference satellite uses the DVB receiver, it will need to be
configured as follows:
Figure 5.10.1 – Reference Satellite Profile Example
Notice that the profile name designated this as a Reference satellite profile. Also notice that
all acquisition sources are selected for the DVB receiver, except “Fine Source”. For a faster
(reference sat) acquisition, “Fine Source” may be set to none. Also see Appendix H for
complete DvB ref sat setup.
Since the generic “high band” frequency of 12235MHz (1485MHz L-band with a 10750MHz
LNB LO) is selected for level and not DVB coding, the “Enable DvB Mode” function of the
receiver is turned off as well as the “Signal Optimization” function. In this mode, the receiver
performs much like a narrow band beacon receiver.
















































