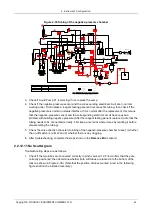
2 Instrument Configuration
Copyright © WOODLEY EQUIPMENT COMPANY LTD.
34
3. After soaking it for five minutes or so, restore the original tubing.
4. Click the error message area, and then click
Remove Error
in the pop-up dialog box to see if the
problem has been resolved. If the problem persists, keep taking the aforementioned steps until
the problem has been resolved.
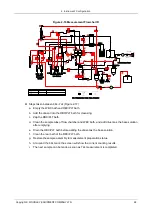
2.2.12.5 Aperture Clogging of the RBC Channel
Aperture clogging can be resolved by implementing the procedure for cleaning the RBC bath. The
procedures are shown as below:
1. Go to
Service
>
Maintenance
>
Clean
and click the
Clean
RBC bath
button.
2. Go to the
Service
>
Maintenance
>
Maintain
screen, and click the
Zap Apertures
button.
3. After you are done, click the error message area, and then click
Remove Error
in the pop-up
dialog box to see if the clogging problem is resolved.
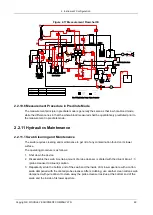
If clogging persists, the probe cleanser needs to be manually pushed through to clean the
RBC-channel aperture, and the following steps should be taken:
4. Empty the RBC bath.
There are two ways of emptying the RBC bath:
➢
Go to the
Service
>
Maintenance
>
Maintain
screen, click the
Empty RBC Bath
button
(note that a prompt box will pop up for confirmation after draining; do not press the
OK
button, otherwise the RBC bath will be refilled with liquid).
➢
The liquid can also be aspirated dry manually using a plastic syringe or other tools.
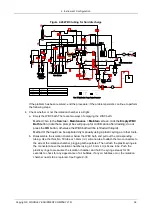
5. Pull out the tubing connected to the RBC outflow tube and connect the plastic syringe filled with
the diluted probe cleanser (with a ratio of probe cleanser to diluent of 1:3) to the RBC outflow
tube (as shown in Figure 2-28). Pushing the plastic syringe back and forth will facilitate the
repeated flushing of the aperture with the probe cleanser.
Figure 2-28 Cleaning the RBC-bath aperture
Apply proper force while pushing to prevent the tube from dropping and spilling (you can hold the
tube with your hand to keep it in place).