8-4 | MVW3000
88
Special Functions
Line AC
Input
cubicle
Transformer
Inverter
Bypass
reactor
Inverter
contactor
Line contactor
(Bypass)
MVW3000
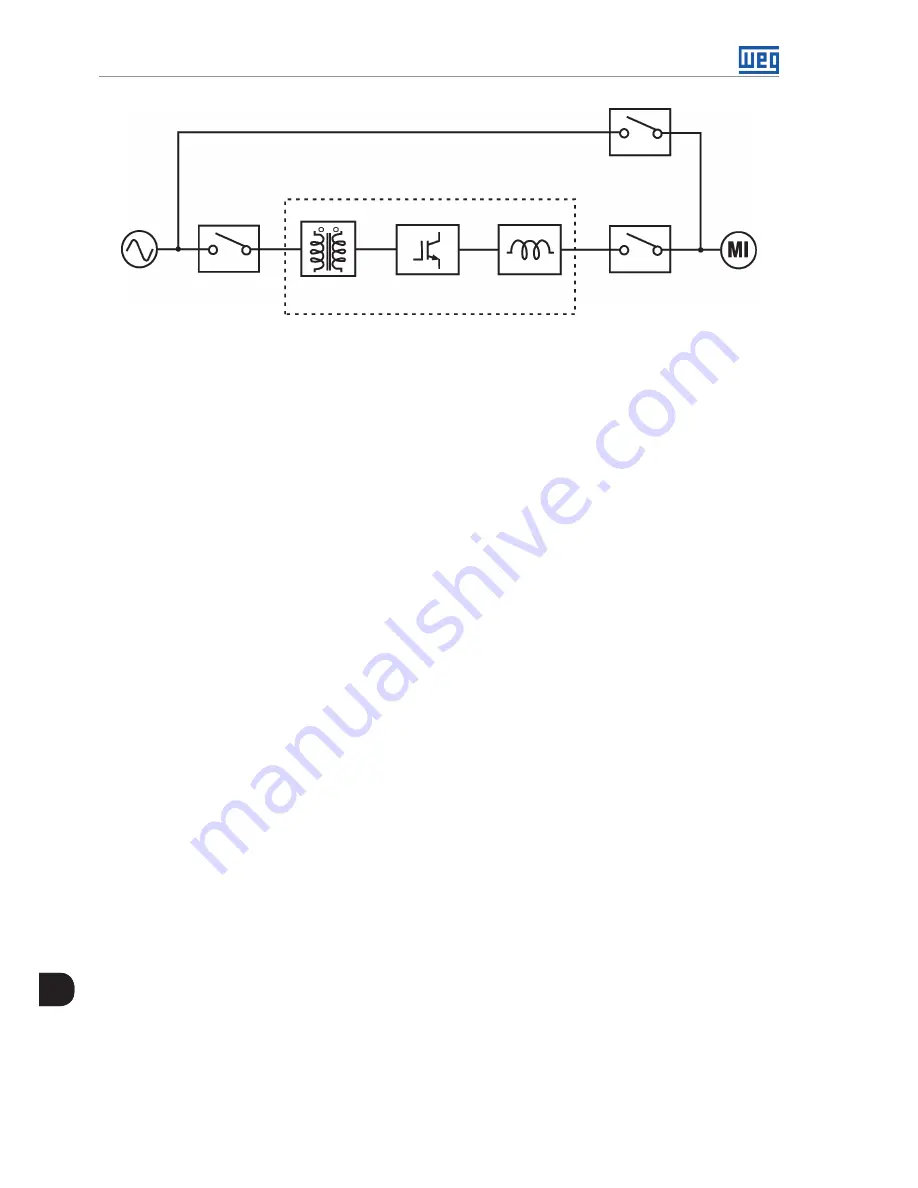
Figure 8.4:
General scheme of synchronous transfer
Basic Settings
The synchronous transfer process involves accelerating the motor up to the rated speed, synchronizing the
voltage imposed to the motor with the line voltage, and making the transfer to the line. For the transfer to occur
properly and with minimal impact on the motor and on the inverter, a series of parameters must be carefully
adjusted so as to ensure the phase synchronization, the minimum difference of the RMS value between the
inverter and the line voltages and the timely occurrence of each step of the process.
Even with the correct setting of parameters related to the synchronous transfer process, it is necessary to use
a reactor between the inverter and the motor in order to absorb differences between the inverter and the line
voltage, thus protecting the inverter during the closing of the line contactor.
Therefore, after making all the start-up procedure for inverter with operation in normal mode, it is necessary to:
Configure the motor voltage (P0400) equal to the line voltage to which the motor will be transferred. In the
operation with synchronous bypass, the inverter uses this value to calculate the RMS voltage that will be
imposed to the motor when operating at rated frequency.
E.g.: motor nameplate voltage of 4000 V and line of 4160 V. Configure P0400 = 4160 V.
Configure the inverter in synchronous transfer mode.
Choose one of the DIs available on the MVC4 board (DI3 to DI10) and configure it to start the synchronous
transfer
(P0265 to P0272 = 23 or 25)
.
Configure one DO (RL1 to RL5) to indicate that the synchronism with the line is “OK”
(P0277 to P0282 = 34)
.
Parameterization Used for Most Applications
In addition to the aforementioned basic settings, other parameters must be set for the correct operation of the
function. Below is a quick description of each parameter, as well as the setting used in most applications.
P0629 = 2 s
Minimum time for which the inverter will have to keep the phase error between the input and
output voltage lower than the setting in P632 so as to signal synchronism OK.
P0630 = 60 s
Synchronism with the network time out. Time counted from the drive of the MVC4 DI, which
starts searching until the signaling of synchronism OK. If this time is exceeded, A0008 will be indicated.
P0631 = adjusted in the application
Delay of DI13 of the PIC2 board used to disable the inverter after the
bypass. This time is used to compensate the delay of the bypass circuit, preventing the motor from remaining
for a period without voltage.
P0632 = 1966
Phase error between the network and inverter voltage used in conjunction with P0629 to indicate
synchronism OK.
(P0632/65536)*360º = value in degrees
.
Summary of Contents for MVW3000 A0040 V023
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 5: ...User s Manual Series MVW3000 Language English Document 10004823674 00 Publication Date 03 2017...
Page 6: ...Summary of Reviews Version Review Description R00 First edition...
Page 12: ...1 4 MVW3000 1 Safety Notices...
Page 58: ...6 18 MVW3000 6 Installation Connection and Energization...
















































