RS485 against RS422
RS485 and RS422 are both the electric element and the physical support of the protocol.
The RS485 protocol is equipped with two connections, A and B. Very often, there is also a ground connection (N on EXO
devices). The RS485 connection is as follows A -> A and B -> B. The RS485 protocol is called “half-duplex connection”:
in fact the communication can take place only in one direction at a time, i.e. the master device sends a query and then
waits for an answer. A and B are used both for transmission and for reception.
RS422 is a communication called “full-duplex connection” that requires the use of four wires, two for transmitting (Tx+
and Tx-) and two for receiving (Rx+ and Rx-). “Tx” means transmission and “Rx” reception, therefore the Tx of a machine
must be connected to the Rx of the other machine and vice versa. In terms of signal layers RS422 and RS485 are
identical.
To combine RS422 and RS485: On the RS422 unit, connect Tx+ with Rx+ and Tx- with Rx-, at this point it is necessary
to convert a four-wire system into a two-wire system, in order to be able to connect them on A and B of the device with
RS485. Often it takes several tries before finding the exact final connection. A polarity reversal results in the system not
working, but it cannot damage the device.
Tx+ ---------1 -----------------------------------A (or B)
|
Rx ----------|
Tx-----------1 -----------------------------------B (or A)
|
Rx ----------|
Transmission speed, two stop bits and parity constitute the next layer.
These settings must match those of the master device. Review the master device settings and configure the controller in
the same way.
The parity can be set to odd, even (RU) or no parity. In the latter case, it is usually set on two stop bits, but it is not
compulsory. If parity is set to “odd” or “even”, only one stop bit will be used to limit the total number of bits: 1 start bit,
8 data bits, 1 parity bit and a stop bit representing a total of 11 bits, which is the maximum.
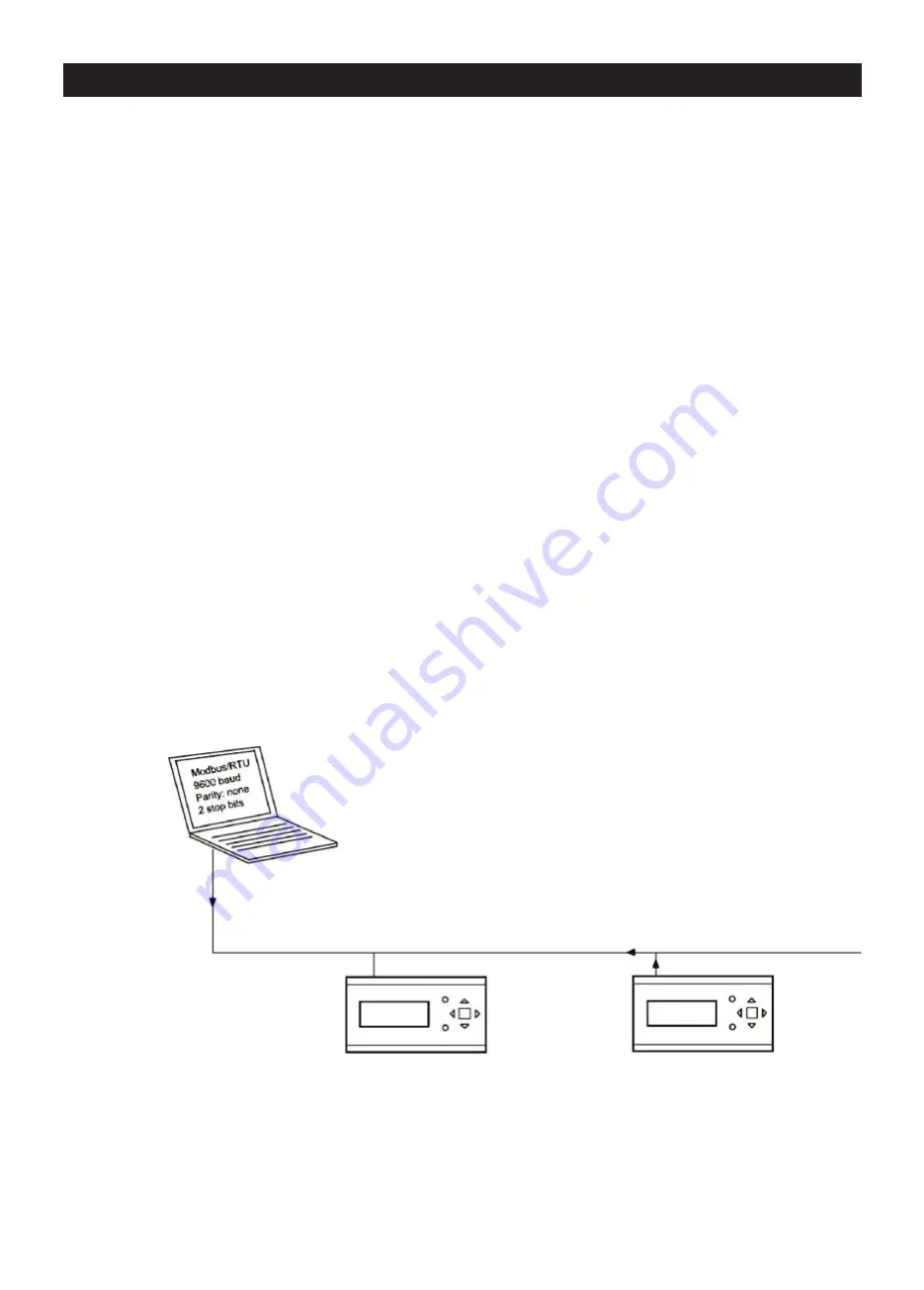
Example
The following simplified example illustrates the master-slave relationship. In addition, a control sum used to validate the
message is transmitted with the query and the answer.
ENGLISH
Query:
“Reading from point x
address on slave 2
address”
Answer:
“The slave 1 address
contains the z value on the
address of the required point”
Corrigo E
Slave Address: 1
Modbus/RTU 9600 baud
Parity: none 2 stop bit
Corrigo E
Slave Address: 2
Modbus/RTU 9600 baud
Parity: none 2 stop bit
46
Summary of Contents for VORT NRG EC 3000
Page 37: ...X NOTES GRAPHS AND COMMUNICATION DIAGRAMS ENGLISH Date Observations 37...
Page 39: ...ENGLISH REPEATER RS485 100 metres Maximum 6 control units MASTER Ext Disp REPEATER 39...
Page 40: ...ENGLISH BMS LON 100 metres MASTER Ext Disp LON EXTENSION OU 40...
Page 54: ...54 NOTE ENGLISH...
Page 84: ...X REMARQUES GRAPHIQUES ET DIAGRAMMES DE COMMUNICATION 84 FRAN AIS Date Observations...
Page 86: ...FRAN AIS R P TEUR RS485 100 m tres Maximum 6 centrales MA TRE Ext Disp R P TEUR 86...
Page 87: ...FRAN AIS BMS LON 100 m tres MASTER Ext Disp EXTENSION LON OU 87...
Page 101: ...101 IX NOTE FRAN AIS...
Page 131: ...X NOTIZEN SCHAUBILDER UND KOMMUNIKATIONSDIAGRAMME DEUTSCH Datum Anmerkungen 131...
Page 134: ...DEUTSCH BMS LON 100 Meter MASTER Ext Disp ERWEITERUNG LON OU 134...
Page 148: ...148 IX NOTE DEUTSCH...
















































