Page 108
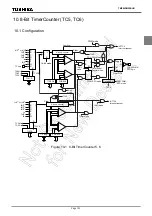
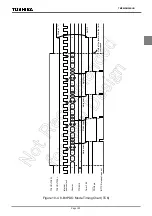
10. 8-Bit TimerCounter (TC5, TC6)
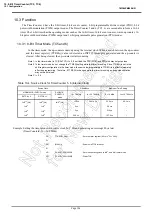
10.1 Configuration
TMP86PM29BUG
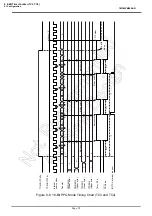
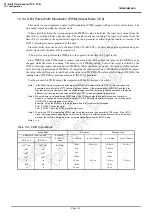
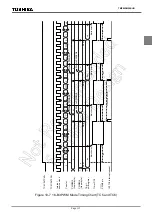
Note 1: In the programmable divider output mode, do not change the TTREGj setting while the timer is running.
Since TTREGj is not in the shift register configuration in the programmable divider output mode, the new
value programmed in TTREGj is in effect immediately after programming. Therefore, if TTREGi is changed
while the timer is running, an expected operation may not be obtained.
Note 2: When the timer is stopped during PDO output, the
PDOj
pin holds the output status when the timer is
stopped. To change the output status, program TCjCR<TFFj> after the timer is stopped. Do not change the
TCjCR<TFFj> setting upon stopping of the timer.
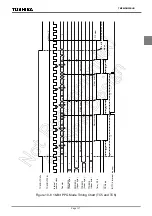
Example: Fixing the
PDOj
pin to the high level when the TimerCounter is stopped
CLR (TCjCR).3: Stops the timer.
CLR (TCjCR).7: Sets the
PDOj
pin to the high level.
Note 3: j = 6
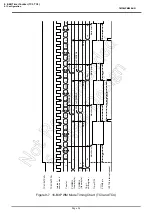
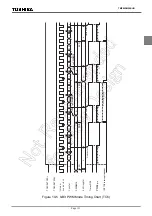
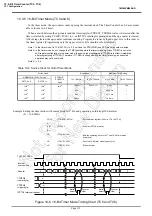
Example :Generating 1024 Hz pulse using TC6 (fc = 16.0 MHz)
Setting port
LD
(TTREG6), 3DH
: 1/1024
÷
2
7
/fc
÷
2 = 3DH
LD
(TC6CR), 00010001B
: Sets the operating clock to fc/2
7
, and 8-bit PDO mode.
LD
(TC6CR), 00011001B
: Starts TC6.
Summary of Contents for TLCS-870/C Series
Page 1: ...8 Bit Microcontroller TLCS 870 C Series TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 6: ...TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 7: ...Revision History Date Revision 2007 10 11 1 First Release 2008 8 29 2 Contents Revised ...
Page 9: ......
Page 15: ...vi ...
Page 19: ...Page 4 1 3 Block Diagram TMP86PM29BUG 1 3 Block Diagram Figure 1 2 Block Diagram ...
Page 23: ...Page 8 1 4 Pin Names and Functions TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 48: ...Page 33 TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 49: ...Page 34 2 Operational Description 2 3 Reset Circuit TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 61: ...Page 46 3 Interrupt Control Circuit 3 8 External Interrupts TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 81: ...Page 66 6 Watchdog Timer WDT 6 3 Address Trap TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 135: ...Page 120 10 8 Bit TimerCounter TC5 TC6 10 1 Configuration TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 145: ...Page 130 11 Asynchronous Serial interface UART 11 9 Status Flag TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 165: ...Page 150 13 10 bit AD Converter ADC 13 6 Precautions about AD Converter TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 183: ...Page 168 15 LCD Driver 15 4 Control Method of LCD Driver TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 201: ...Page 186 18 Electrical Characteristics 18 9 Handling Precaution TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 203: ...Page 188 19 Package Dimensions TMP86PM29BUG ...
Page 205: ......