Structural Maintenance
12-23
Closing the Damper Door
When a Defrost cycle is initiated 12 volts is supplied to the A terminal of the gear motor controller via the 29 wire. The gear
motor controller then supplies chassis ground to the gear motor via the Y terminal to energize the motor. The gear motor
controller ignores the amount of current drawn for the first few seconds of operation to accommodate the current spikes that may
result if the damper is frozen in position.
After this initial “break away” time, the gear motor controller then monitors current while the motor continues to close the damper
door. When the door is completely closed the motor will stall, causing an increase in the motor current. This current increase
indicates to the gear motor controller that the damper door has reached the fully closed position. The gear motor controller then
removes chassis ground from the motor at the controller Y terminal. 12-Vdc power is again present at both sides of the gear motor.
Opening the Damper Door
When a Defrost cycle is complete 12 volts is supplied to the B terminal of the gear motor controller via the 29A wire. The gear
motor controller then supplies ground to the gear motor via the X terminal to energize the motor. The gear motor controller
monitors current while the motor opens the damper door. When the door is completely open the motor will again stall, causing
an increase in the motor current. This current increase indicates to the gear motor controller that the damper door has reached the
fully open position. The gear motor controller then removes chassis ground from the motor at the controller X terminal. 12 Vdc
power is again present at both sides of the gear motor.
Diagnostics
The only tool required is an accurate digital multi-meter such as a Fluke.
Refer to the electrical schematics and wiring diagrams for the specific unit.
Voltages are measured from the specified gear motor controller terminal to chassis ground. Proceed in the order shown below:
1. Disconnect the GM+ wire at the “X” terminal of the controller. Measure the resistance of the gear motor from the GM+ wire
to the “Y” terminal of the controller. If the motor resistance is not approx. 6.0 ohms the motor or motor harness is defective
and must be repaired or replaced.
2. Reconnect the GM+ wire to the “X” terminal of the controller.
3. Be sure a secure connection exists from the “-” terminal of the controller to chassis ground.
4. Start the unit and use Service Test mode to place the unit in Low Speed Cool. See Service Procedure in the relevant
microprocessor Diagnostic Manual for details of using Service Test mode.
5. Battery voltage should be present at the “B” terminal (29A wire) of the controller. If not, check the defrost relay K3 located
on the relay board.
6. Battery voltage should be present at the “+” terminal (HGP wire) of the controller. If not, check the unit 8F and HGP circuits.
7. Battery voltage should be present at both the “X” (GM+ wire) and “Y” (GM- wire) terminals of the controller. If not, the
controller is defective and must be replaced.
8. Place the unit in Defrost using Service Test mode. Battery voltage should be present at the “A” terminal (29 wire) of the
controller. If not, check the defrost relay K3 located on the relay board.
9. Place the unit in Low Speed Cool using Service Test mode.
10. Connect the voltmeter to the “Y” terminal (GM- wire) of the controller. Carefully monitor the meter and place the unit in
Defrost using Service Test mode. When the defrost relay is energized the voltage from the “Y” terminal to ground should fall
below 0.5-vdc for 3 to 10 seconds. If not, the controller is defective and must be replaced.
11. Connect the voltmeter to the “X” terminal (GM+ wire) of the controller. Carefully monitor the meter and place the unit in
Low Speed Cool using Service Test mode. When the defrost relay is energized the voltage from the “X” terminal to ground
should fall below 0.5-vdc for 3 to 10 seconds. If not, the controller is defective and must be replaced.
12. Check to be sure the linkage is connected correctly. Note that due to the gear reduction involved moving the defrost damper
door manually is impossible.
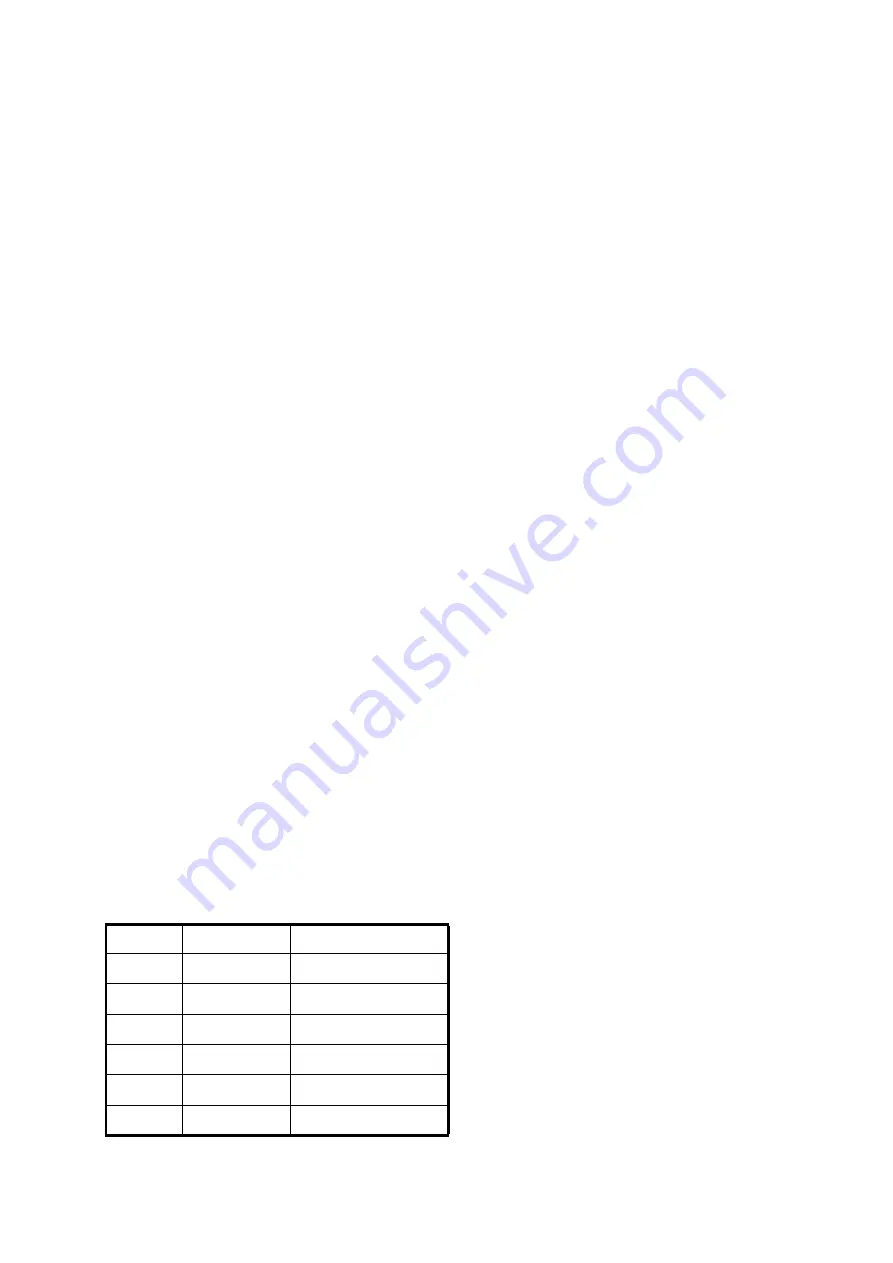
Gear Motor Controller Connections
Terminal
Description
Wire
A
Close Signal
29
B
Open Signal
29A
+
Power
8F/HGP
-
Chassis Ground
CH
X
+ Motor Lead
GM+ (BLK Motor Wire)
Y
- Motor Lead
GM- (RED Motor Wire)
Summary of Contents for SLXi Spectrum
Page 17: ...Safety Precautions 2 5 Warning Decals...
Page 18: ...Safety Precautions 2 6 Warning Decals Information Decals...
Page 74: ...Unit Description 5 30...
Page 128: ...Controller Operation 7 28...
Page 156: ...Electrical Maintenance 8 28...
Page 234: ...Refrigeration Maintenance 10 22...
Page 309: ...13 Mechanical Diagnosis TK 482 TK 486 and TK 486V Engines 13 2...
Page 316: ...Mechanical Diagnosis 13 8...
Page 322: ...Refrigeration System Diagnosis 14 6...
Page 332: ...Single Temperature Refrigeration System Diagrams 15 10...
Page 339: ...Multi Temperature Refrigeration System Diagrams 16 7...
Page 340: ...Multi Temperature Refrigeration System Diagrams 16 8...