3.7.5
Safe Direction (SDI)
What is the effect of the SDI safety function?
The inverter with active SLS function monitors the motor direction of rotation. If the motor
rotates in the inhibited direction, the inverter stops the motor as quickly as possible.
The SDI function therefore prevents that an electrically driven machine component moves in
the inhibited direction.
Table 3-8
An overview of the principle of operation of SDI, selected when the motor is rotating
Safe Direction (SDI)
Standard inverter functions linked with SDI
1. The inverter identifies when SDI is selec‐
ted via a fail-safe input or via safety-rela‐
ted PROFIsafe communication.
---
2. SDI allows a motor to stop moving in the
inhibited direction of rotation within a de‐
fined time – or along a defined braking
ramp.
The inverter limits the speed setpoint to values in the
selected direction of rotation.
If the motor rotates in the inhibited direction, then the
inverter brakes the motor along the OFF3 ramp.
3. The inverter monitors the direction of the
actual speed.
The inverter signals "SDI is active" via a
fail-safe digital output or via PROFIsafe.
If the motor rotates in the inhibited direc‐
tion, the inverter responds with a "safe
stop" and brakes the motor as quickly as
possible.
The inverter limits the speed setpoint to values in the
selected direction of rotation.
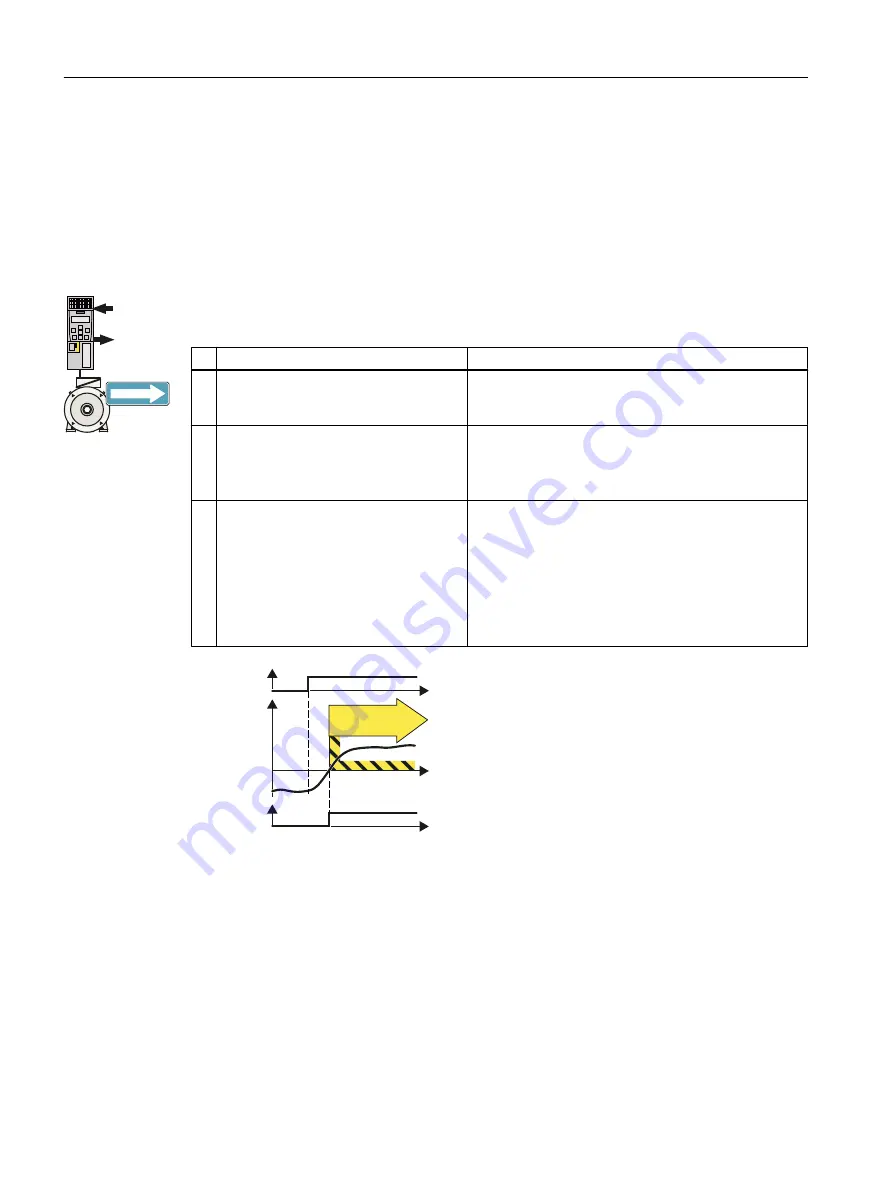
6SHHG
6HOHFW6',
6',LVDFWLYH
SDI
W
W
W
Figure 3-7
Principle of operation of SDI
The SDI safety function is standardized
The SDI function is defined in IEC/EN 61800-5-2:
"The SDI function prevents the motor shaft moving in the wrong direction."
⇒ The SDI inverter function is in conformance with IEC/EN 61800-5-2.
6HOHFW
6',
6',LV
DFWLYH
ONE WAY
Description
3.7 An overview of the principle of operation of the safety functions
Safety Integrated - SINAMICS G110M, G120, G120C, G120D and SIMATIC ET 200pro FC-2
42
Function Manual, 01/2017, FW V4.7 SP6, A5E34261271B AD
















































