44
2 CONTROL MODE
2.1 Control mode [G] [WG]
Homing method list
In the following cases, make sure that the Z-phase has been passed once before performing homing. If the Z-phase has not
been passed, [AL. 090.5 Homing incomplete warning] will occur.
• When using an incremental linear encoder in the linear servo motor control mode
• When using an incremental external encoder in the fully closed loop control mode
• When using a direct drive motor manufactured by Mitsubishi Electric in the direct drive motor control mode
To execute homing securely, move the linear servo motor to the opposite stroke end with csv or other operation modes from
the controller, then start homing. [Digital inputs (Obj. 60FDh)] can be used to check whether the linear servo motor has
reached the stroke end.
When changing the mode after homing finishes, set [Target position (Obj. 607Ah)] to "0", then change the control mode.
If using an A/B/Z-phase differential output rotary encoder without a Z-phase, do not perform dog type homing or homing using
a Z-phase. Doing so may cause the servo motor to keep driving without homing being completed. Perform data set type
homing or homing without using a Z-phase.
If an A/B/Z-phase differential output type encoder is used, the accuracy of homing using the Z-phase depends on the Z-phase
width in relation to the A and B-phases.
To specify the homing method in the homing mode (hm), use [Homing Method (Obj. 6098h)]. The homing methods in the
following table are supported.
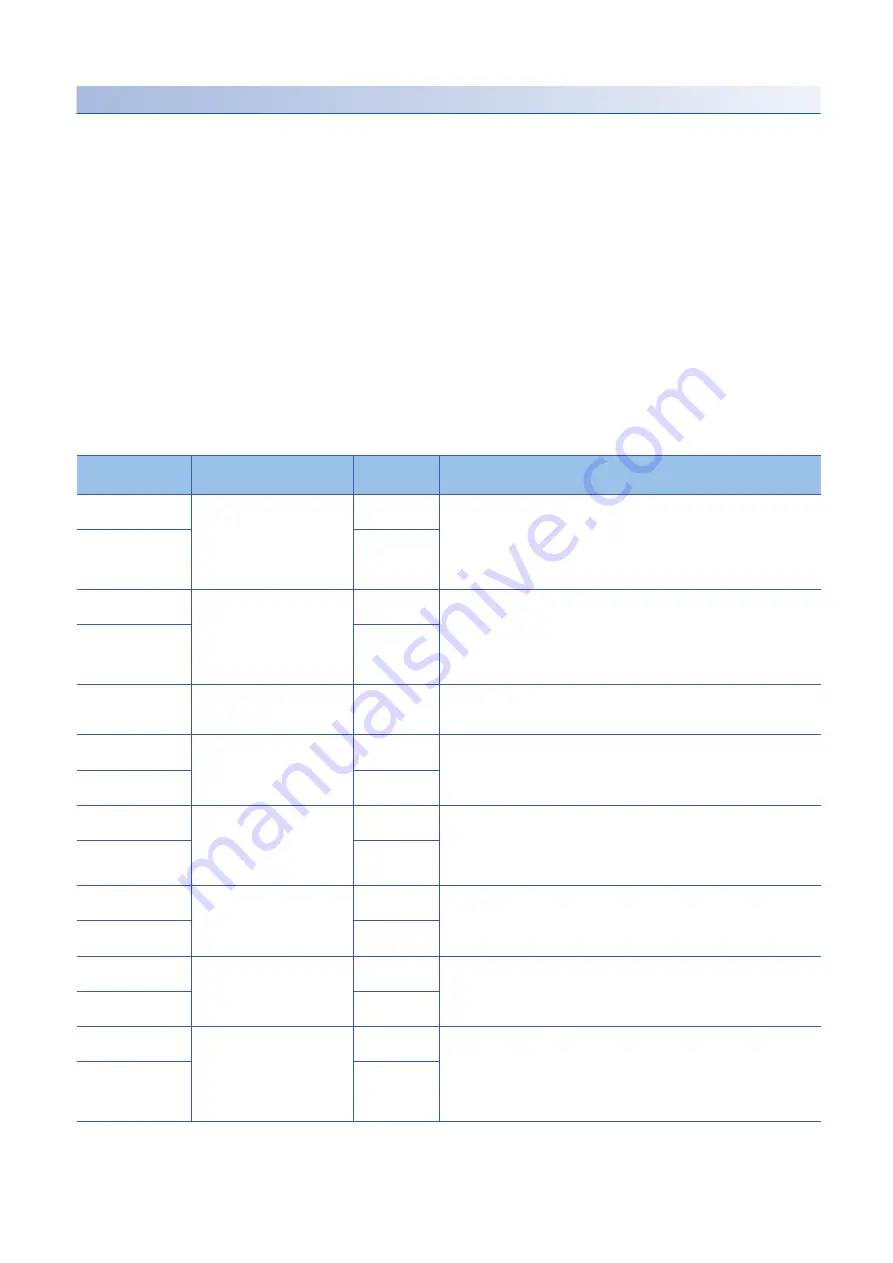
Method No.
Homing methods
Rotation
direction
Description
-1
Dog type homing
(Rear end detection - Z-phase
reference)
Forward
rotation
Performs homing using the Z-phase pulse after a moving part has moved past
the proximity dog.
Deceleration starts from the front end of the proximity dog. After the rear end is
passed, the position specified by the first Z-phase signal or the position of the
first Z-phase signal shifted by the specified home position shift distance is used
as the home position.
-33
Reverse
rotation
-2
Count type homing
(Front end detection - Z-phase
reference)
Forward
rotation
Performs homing using the encoder pulse count after a moving part came into
contact with the proximity dog.
Deceleration starts from the front end of the proximity dog. After the front end is
passed, the position specified by the first Z-phase signal after the set distance or
the position of the Z-phase signal shifted by the set home position shift distance
is set as the home position.
-34
Reverse
rotation
-3
Data set type homing
Performs homing without a dog.
The current position is set as the home position.
This is the same as Homing methods 35 and 37.
-4
Stopper type homing
(Stopper position reference)
Forward
rotation
Performs homing with a workpiece pressed against a mechanical stopper.
A workpiece is pressed against a mechanical stopper, and the stop position is
set as the home position.
-36
Reverse
rotation
-6
Dog type homing
(Rear end detection - rear end
reference)
Forward
rotation
Performs homing with reference to the rear end of the proximity dog.
Deceleration starts from the front end of the proximity dog. After the rear end is
passed, the position is shifted by the travel distance after proximity dog and the
home position shift distance. The position after the shifts is set as the home
position.
-38
Reverse
rotation
-7
Count type homing
(Front end detection - front end
reference)
Forward
rotation
Performs homing with reference to the front end of the proximity dog.
Deceleration starts from the front end of the proximity dog. The position is
shifted by the travel distance after the proximity dog and the home position shift
distance. The position after the shifts is set as the home position.
-39
Reverse
rotation
-8
Dog cradle type homing
Forward
rotation
Performs homing using the first Z-phase pulse with reference to the front end of
the proximity dog.
A position, which is specified by the first Z-phase signal after the front end of the
proximity dog is detected, is set as the home position.
-40
Reverse
rotation
-9
Dog type last Z-phase reference
homing
Forward
rotation
Performs homing using the last Z-phase pulse with reference to the front end of
the proximity dog.
After the front end of the proximity dog is detected, the position is shifted away
from the proximity dog in the reverse direction. Then, the position specified by
the first Z-phase signal or the position of the first Z-phase signal shifted by the
home position shift distance is used as the home position.
-41
Reverse
rotation
















































