COMe-mAL10 – User Guide, Rev. 1.3
www.kontron.com
// 33
3/
Features and Interfaces
3.1.
eMMC Flash Memory
An optional embedded Multimedia Flash Card (eMMC) complying with the eMMC 5.0 specification can be permanently
attached to the module, allowing for a capacity of up to 64 GByte NAND Flash. During the COMe-mAL10’s
manufacturing process, Multi Level Cell (MLC) eMMC is reconfigured to act as pseudo Single Level Cell (pSLC) eMMC
to provide improved reliability, endurance and performance.
General eMMC Flash memory features are:
2 GByte to 64 GByte pSLC (or 4 GByte to 128 GByte MLC)
eMMC 5.0 compatible
3.2.
LPC
The Low Pin Count (LPC) Interface signals are connected to the LPC bus bridge located in the CPU or integrated
chipset. The LPC low speed interface can be used for peripheral circuits such as an external Super I/O controller that
typically combines legacy-device support into a single IC. The implementation of this subsystem complies with the
COM Express® Specification. For more information, refer to the COM Express® Design Guide maintained by PICMG or
the official PICMG documentation.
The LPC bus does not support DMA (Direct Memory Access). When more than one device is used on LPC, a zero delay
clock buffer is required that can lead to limitations for the ISA bus.
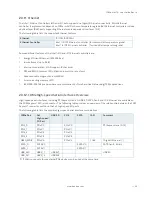
Table 15: Supported BIOS Features
Interface Signals
AMI EFI APTIO V
PS/2
Not supported
COM1/COM2
Supported as COM3 and COM4 (COM1/COM2 are already on-board)
LPT
Not supported
HWM
Not supported
Floppy
Not supported
GPIO
Not supported
Features marked as not supported do not exclude OS support, except for, HWM that is controlled by the BIOS setup
within the Advanced setup menu and has no OS software support. The HWM is accessible via the System
Management (SM) Bus, for more information see chapter 4.6 System Management (SM) Bus. If any other LPC Super
I/O additional BIOS implementations are necessary contact Kontron Support.
3.3.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
The Serial Peripheral Interface Bus (SPI bus) is a synchronous serial data link standard. Devices communicate in
master/slave mode, where the master device initiates the data frame. Multiple slave devices are allowed with
individual slave select (chip select) lines. SPI is sometimes called a four-wire serial bus, contrasting with three, two
and one-wire serial buses.
The SPI interface can only be used with a SPI Flash device to boot from the external BIOS on
the baseboard.