Chapter 5. FUNCTIONS
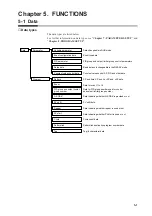
5-2 Program Pattern
■
Pattern
Three systems for selecting programs are provided: RAMP-X, RAMP-T and RAMP-E.
The first segment of each program is always RAMP-X, but the other segments can be
any system and all three types can be used in one program.
●
RAMP-X system
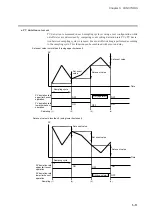
This system, sets a segment of a pattern using SP and time, is called RAMP-X.
SP setting
: within the upper and lower SP limiter range
Time setting : 0 hours 00 minutes to 500 hours 00 minutes
0 minutes 00 seconds to 500 minutes 00 seconds or
0.0 seconds to 3000.0 seconds
(Time units are selected using the
C62
setup data setting.)
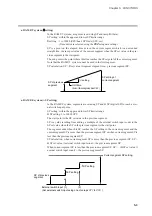
SP is a point on the elapsed time axis in the current segment, which is a straight line con-
necting the start point, the SP set value in the previous segment, and the end point, the
SP set value in the current segment. Segments are classified as follows.
• Rising RAMP (or rising slope)
Previous segment SP setting < current segment SP setting
• Falling RAMP (or descending slope)
Previous segment SP setting > current segment SP setting
• SOAK (soaking)
Previous segment SP setting = current segment SP setting
The start and end points of the first segment are also the SOAK segment of the SP set
value for the first segment.
SP calculation (other than first segment)
SP = (current segment SP set value – previous segment SP set value)
×
(current segment elapsed time ÷ current segment time setting)
+ previous segment SP setting.
5-2