Section 4
♦
Operating the CMN-41
CMN-41 Series Installation and Operation Handbook
43
Copyright © 2009, Harris Corporation
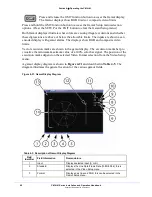
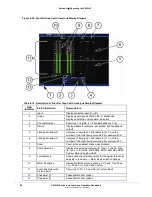
(which are in mV) in a polar format to represent color information. The rings turn red
when the alarm is enabled and the values exceed the threshold setting.
Each R, G, and B pixel is plotted using amplitude and phase. The amplitude is derived
from the R, G, B component. The phase is derived from the C
B
C
R
information of the
digital signal. The pixels can be plotted as a single color or as each component color
(see
Table 5-8
on page 67). Unlike the composite Gamut vector, which plots two
points per pixel, the RGB Gamut vector plots three points. Also, signals with no color
content are displayed on a separate bar graph labeled Mono.
The RGB graticule is nearly identical to the composite graticule. The only differences are
•
Amplitudes are displayed in mV rather than IRE or UNITS.
•
The radials representing color vectors are 60° apart since they are displayed in a
component color space.
•
Mono bar graph is for monochrome.
NOTE
: There is an alarm persistence of two seconds associated with any alarm indication. After an alarm
has cleared, two seconds will pass before the gamut indicator returns to normal.
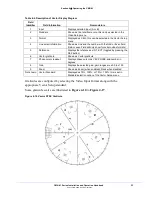
Figure 4-23. Component (RGB) Gamut Vector Display Graticule Markings
Table 4-7. Description of RGB Gamut Indicators
Key Indicator
Description
1
Lower Gamut Ring
The lower gamut ring indicates the RGB Gamut alarm Lower limit.
When the RGB Gamut alarm is enabled and the Lower limit is
exceeded, the lower gamut ring turns red.
2
Upper Gamut Ring
The upper gamut ring indicates the RGB Gamut alarm Upper limit.
When the RGB Gamut alarm is enabled, and the Upper limit is
exceeded, the upper gamut ring turns red.
3
Vector Excursion Mark
The excursion marks help to visualize the minimum/maximum
values of 100% color bars.
4
Mono
Mono indicates the monochrome of the RGB signal. There is no
alarm associated with Mono.