GE Multilin
F60 Feeder Protection System
B-61
APPENDIX B
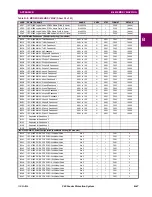
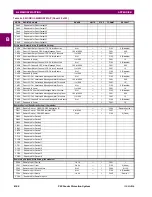
B.4 MEMORY MAPPING
B
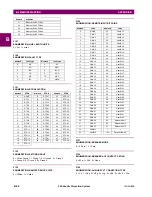
F012
DISPLAY_SCALE DISPLAY SCALING
(unsigned 16-bit integer)
MSB indicates the SI units as a power of ten. LSB indicates the
number of decimal points to display.
Example: Current values are stored as 32 bit numbers with three
decimal places and base units in Amps. If the retrieved value is
12345.678 A and the display scale equals 0x0302 then the dis-
played value on the unit is 12.35 kA.
F013
POWER_FACTOR (SIGNED 16 BIT INTEGER)
Positive values indicate lagging power factor; negative values
indicate leading.
F040
UR_UINT48 48-BIT UNSIGNED INTEGER
F050
UR_UINT32 TIME and DATE (UNSIGNED 32 BIT INTEGER)
Gives the current time in seconds elapsed since 00:00:00 January
1, 1970.
F051
UR_UINT32 DATE in SR format (alternate format for F050)
First 16 bits are Month/Day (MM/DD/xxxx). Month: 1=January,
2=February,...,12=December; Day: 1 to 31 in steps of 1
Last 16 bits are Year (xx/xx/YYYY): 1970 to 2106 in steps of 1
F052
UR_UINT32 TIME in SR format (alternate format for F050)
First 16 bits are Hours/Minutes (HH:MM:xx.xxx).
Hours: 0=12am, 1=1am,...,12=12pm,...23=11pm;
Minutes: 0 to 59 in steps of 1
Last 16 bits are Seconds (xx:xx:.SS.SSS): 0=00.000s,
1=00.001,...,59999=59.999s)
F060
FLOATING_POINT IEEE FLOATING POINT (32 bits)
F070
HEX2 2 BYTES - 4 ASCII DIGITS
F071
HEX4 4 BYTES - 8 ASCII DIGITS
F072
HEX6 6 BYTES - 12 ASCII DIGITS
F073
HEX8 8 BYTES - 16 ASCII DIGITS
F074
HEX20 20 BYTES - 40 ASCII DIGITS
F080
ENUMERATION: AUTORECLOSE MODE
0 = 1 & 3 Pole, 1 = 1 Pole, 2 = 3 Pole-A, 3 = 3 Pole-B
F083
ENUMERATION: SELECTOR MODES
0 = Time-Out, 1 = Acknowledge
F084
ENUMERATION: SELECTOR POWER UP
0 = Restore, 1 = Synchronize, 2 = Sync/Restore
F086
ENUMERATION: DIGITAL INPUT DEFAULT STATE
0 = Off, 1 = On, 2= Latest/Off, 3 = Latest/On
F090
ENUMERATION: LATCHING OUTPUT TYPE
0 = Operate-dominant, 1 = Reset-dominant
F100
ENUMERATION: VT CONNECTION TYPE
0 = Wye; 1 = Delta
F101
ENUMERATION: MESSAGE DISPLAY INTENSITY
0 = 25%, 1 = 50%, 2 = 75%, 3 = 100%
Summary of Contents for F60 UR Series
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 30: ...1 20 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 1 5 USING THE RELAY 1 GETTING STARTED 1 ...
Page 48: ...2 18 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 2 2 SPECIFICATIONS 2 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 2 ...
Page 126: ...4 30 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 4 2 FACEPLATE INTERFACE 4 HUMAN INTERFACES 4 ...
Page 354: ...5 228 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 5 9 TESTING 5 SETTINGS 5 ...
Page 382: ...6 28 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 6 5 PRODUCT INFORMATION 6 ACTUAL VALUES 6 ...
Page 398: ...8 8 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 8 2 FAULT LOCATOR 8 THEORY OF OPERATION 8 ...
Page 414: ...A 14 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin A 1 PARAMETER LIST APPENDIXA A ...
Page 492: ...B 78 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin B 4 MEMORY MAPPING APPENDIXB B ...
Page 530: ...D 10 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin D 1 IEC 60870 5 104 APPENDIXD D ...
Page 542: ...E 12 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin E 2 DNP POINT LISTS APPENDIXE E ...
Page 558: ...x F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin INDEX ...