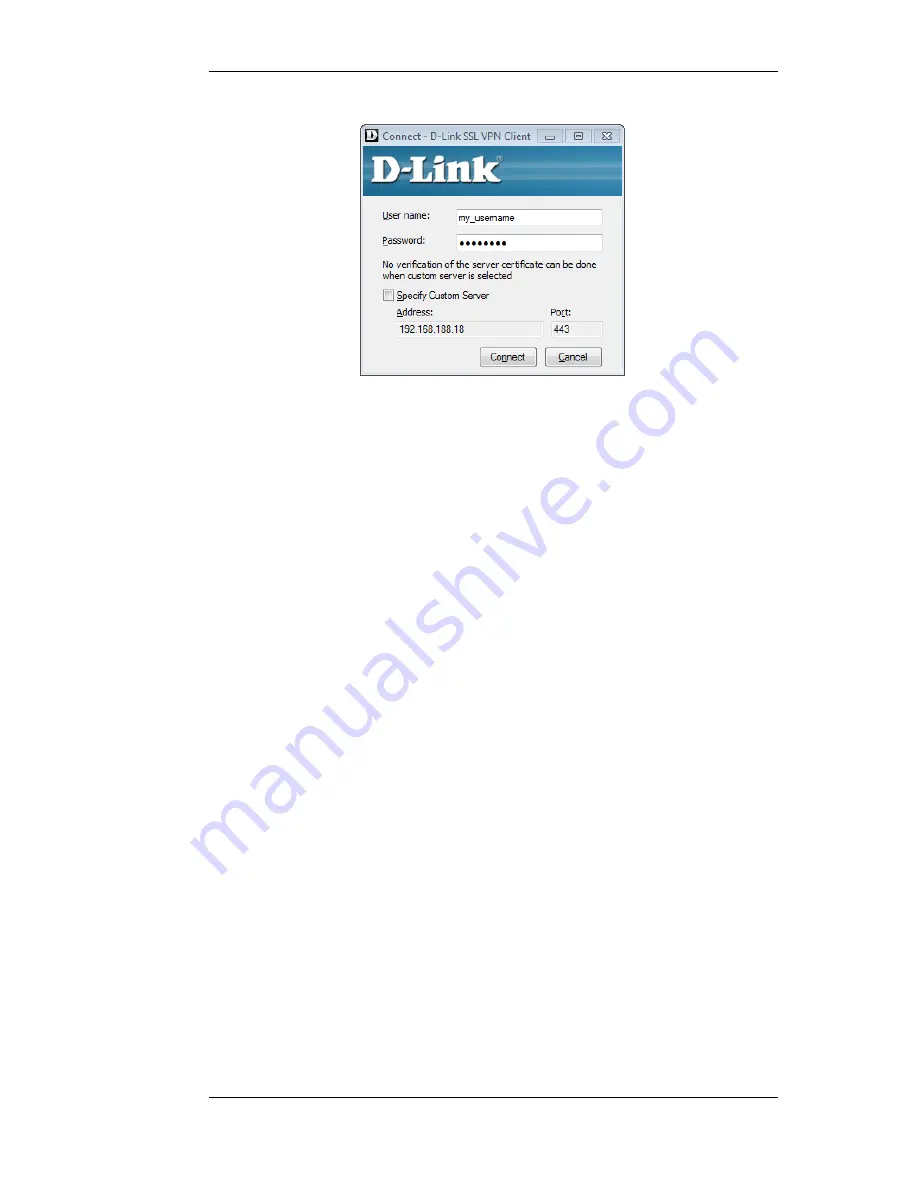
Figure 9.5. The SSL VPN Client Login
The difference between the two approaches above is that when the SSL VPN client software is
started by browsing to the SSL VPN interface, the correct settings for the tunnel are downloaded to
the SSL VPN client software and stored as the client's configuration file.
As long as these settings have not changed between tunnel sessions, it is possible to start the SSL
VPN client software running by selecting it in the Start menu and connecting to the same SSL VPN
interface. In particular, the SSL VPN client checks the certificate used by the SSL VPN interface by
comparing a certificate fingerprint stored in the configuration file with a fingerprint sent by the
interface.
The reason for checking the certificate in this way is that it solves the "man in the middle" problem
where a malicious third party might try to intercept communications between the firewall and the
client.
Custom Server Connection
When the SSL VPN client software is started, it is possible to connect to an SSL VPN interface on a
NetDefend Firewall that has not been connected to before. This is done by enabling the option
Specify Custom Server and explicitly specifying the IP address, port and login credentials for the
server.
With the Specify Custom Server option enabled, the SSL VPN client ignores any configuration file
parameters previously downloaded by an SSL VPN connection established using the web interface.
In particular, it does not check the certificate used by the firewall.
The disadvantage of using the custom server option is that there is no certificate checking and the
"man in the middle" problem remains.
Client Transfer Statistics
When the SSL VPN client is running, an icon for it will appear in the system tray. Clicking this icon
will bring up the client's interface showing amounts of data transferred since tunnel setup.
9.6.3. Installing the SSL VPN Client
Chapter 9. VPN
476
Summary of Contents for NetDefend DFL-1660
Page 28: ...1 3 NetDefendOS State Engine Packet Flow Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 28 ...
Page 88: ...2 6 3 Restore to Factory Defaults Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 88 ...
Page 166: ...3 10 DNS Chapter 3 Fundamentals 166 ...
Page 254: ...4 7 5 Advanced Settings for Transparent Mode Chapter 4 Routing 254 ...
Page 268: ...5 4 IP Pools Chapter 5 DHCP Services 268 ...
Page 368: ...6 7 Blacklisting Hosts and Networks Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 368 ...
Page 390: ...7 4 7 SAT and FwdFast Rules Chapter 7 Address Translation 390 ...
Page 414: ...8 3 Customizing Authentication HTML Pages Chapter 8 User Authentication 414 ...
Page 490: ...9 8 6 Specific Symptoms Chapter 9 VPN 490 ...
Page 528: ...10 4 6 Setting Up SLB_SAT Rules Chapter 10 Traffic Management 528 ...
Page 544: ...11 7 HA Advanced Settings Chapter 11 High Availability 544 ...
Page 551: ...12 3 5 Limitations Chapter 12 ZoneDefense 551 ...
Page 574: ...Default 512 13 9 Miscellaneous Settings Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 574 ...
Page 575: ...13 9 Miscellaneous Settings Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 575 ...










































