20050401
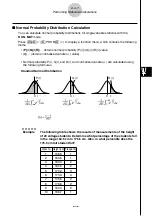
u
u
u
u
u
2-Sample
Z
Test
This test is used when the standard deviations for two populations are known to test the
hypothesis. The
2-Sample
Z
Test
is applied to the normal distribution.
Z
=
o
1
–
o
2
σ
n
1
1
2
σ
n
2
2
2
+
o
1
: mean of sample 1
o
2
: mean of sample 2
σ
1
: population standard deviation of sample 1
σ
2
: population standard deviation of sample 2
n
1
: size of sample 1
n
2
: size of sample 2
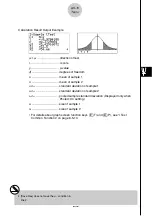
Perform the following key operations from the statistical data list.
3
(TEST)
1
(Z)
2
(2-S)
The following shows the meaning of each item in the case of list data specification.
Data ............................ data type
µ
1
................................. population mean value test conditions (“
G
µ
2
” specifies two-
tail test, “<
µ
2
” specifies one-tail test where sample 1 is
smaller than sample 2, “>
µ
2
” specifies one-tail test where
sample 1 is greater than sample 2.)
σ
1
................................. population standard deviation of sample 1 (
σ
1
> 0)
σ
2
................................. population standard deviation of sample 2 (
σ
2
> 0)
List(1) .......................... list whose contents you want to use as sample 1 data
(List 1 to 26)
List(2) .......................... list whose contents you want to use as sample 2 data
(List 1 to 26)
Freq(1) ........................ frequency of sample 1 (1 or List 1 to 26)
Freq(2) ........................ frequency of sample 2 (1 or List 1 to 26)
Save Res .................... list for storage of calculation results (None or List 1 to 26)
Execute ....................... executes a calculation or draws a graph
6-5-5
Tests
Summary of Contents for fx-9860G AU PLUS
Page 1: ...fx 9860G AU User s Guide E http edu casio com ...
Page 2: ...Important Please keep your manual and all information handy for future reference ...
Page 27: ...20050401 1 1 Keys 1 1 1 Keys ...
Page 335: ...20050401 u u u u u Input Example u u u u u Results 6 5 25 Tests ...
Page 361: ...20050401 Calculation Result Output Example p F distribution probability 6 7 15 Distribution ...
Page 435: ...20050401 8 8 2 Program Library egcw w ww w ...
Page 437: ...20050401 8 8 4 Program Library Example 1 Example 2 fw baw bf w fw baw ca w ...
Page 439: ...20050401 8 8 6 Program Library wba wb w w d ...
Page 441: ...20050401 8 8 8 Program Library dw fcde wfcde wfcde fcde w daw w 20070101 ...
Page 443: ...20050401 8 8 10 Program Library b awaw bwaw aw x d w ...
Page 590: ...CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD 6 2 Hon machi 1 chome Shibuya ku Tokyo 151 8543 Japan SA0701 E ...