20050401
0-1-1
Getting Acquainted
u
Graphs
As a general rule, graph operations are shown on
facing pages, with actual graph examples on the right
hand page. You can produce the same graph on your
calculator by performing the steps under the Procedure
above the graph.
Look for the type of graph you want on the right hand
page, and then go to the page indicated for that graph.
The steps under “Procedure” always use initial RESET
settings.
The step numbers in the “Set Up” and “Execution” sections on the left hand page
correspond to the “Procedure” step numbers on the right hand page.
Example:
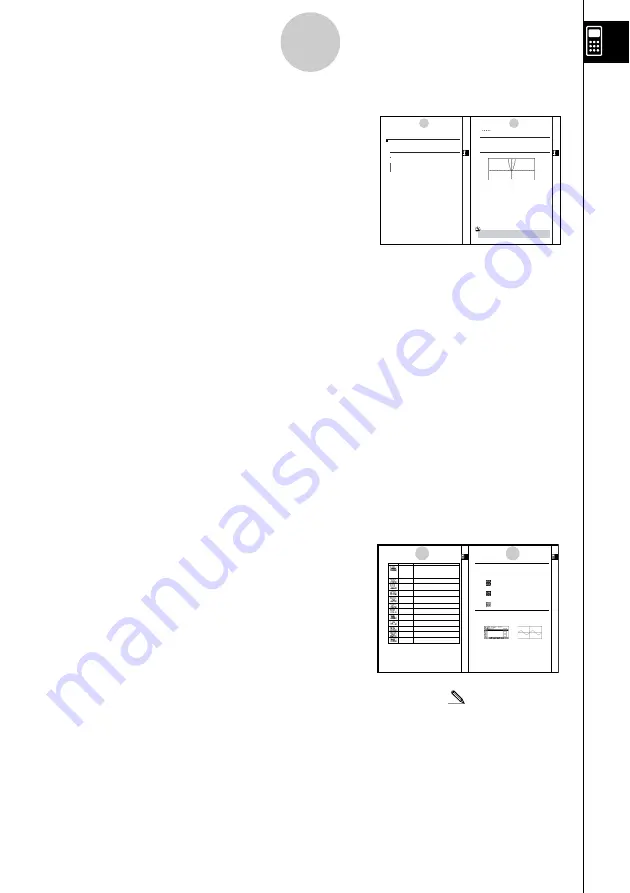
Left hand page
Right hand page
3. Draw the graph.
3
5
(DRAW)(or
w
)
u
u
u
u
u
Command List
The
PRGM
Mode Command List (page 8-7) provides a graphic flowchart of the various
function key menus and shows how to maneuver to the menu of commands you need.
Example: The following operation displays Xfct:
[VARS]
-
[FACT]
-
[Xfct]
u
u
u
u
u
Page Contents
Three-part page numbers are centered at the top of
each page. The page number “1-2-3”, for example,
indicates Chapter 1, Section 2, page 3.
u
u
u
u
u
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information is shown at the bottom of each page in a “
(Notes)” block.
*
indicates a note about a term that appears in the same page as the note.
# indicates a note that provides general information about topic covered in the same section
as the note.
20050401
1-2-2
Display
Icon
Mode Name
Description
S • SHT
Use this mode to perform spreadsheet calculations. Each file
(Spreadsheet)
contains a 26-column
⋅
999-line spreadsheet. In addition to
the calculator’s built-in commands and
S • SHT
mode
commands, you can also perform statistical calculations and
graph statistical data using the same procedures that you use
in the
STAT
mode.
GRAPH
Use this mode to store graph functions and to draw graphs
using the functions.
DYNA
Use this mode to store graph functions and to draw multiple
(Dynamic Graph)
versions of a graph by changing the values assigned to the
variables in a function.
TABLE
Use this mode to store functions, to generate a numeric
table of different solutions as the values assigned to
variables in a function change, and to draw graphs.
RECUR
Use this mode to store recursion formulas, to generate a
(Recursion)
numeric table of different solutions as the values assigned to
variables in a function change, and to draw graphs.
CONICS
Use this mode to draw graphs of conic sections.
EQUA
Use this mode to solve linear equations with two through six
(Equation)
unknowns, quadratic equations, and cubic equations.
PRGM
Use this mode to store programs in the program area and to
(Program)
run programs.
TVM
Use this mode to perform financial calculations and to draw
(Financial)
cash flow and other types of graphs.
to make
LINK
Use this mode to transfer memory contents or back-up data
to another unit or PC.
MEMORY
Use this mode to manage data stored in memory.
SYSTEM
Use this mode to initialize memory, adjust contrast, and to
make other system settings.
20050401
k
k
k
k
k
About the Function Menu
Use the function keys (
1
to
6
) to access the menus and commands in the menu bar
along the bottom of the display screen. You can tell whether a menu bar item is a menu or a
command by its appearance.
• Next Menu
Example:
Selecting
displays a menu of hyperbolic functions.
• Command Input
Example:
Selecting
inputs the sinh command.
• Direct Command Execution
Example:
Selecting
executes the DRAW command.
k
k
k
k
k
About Display Screens
This calculator uses two types of display screens: a text screen and a graph screen. The text
screen can show 21 columns and 8 lines of characters, with the bottom line used for the
function key menu. The graph screen uses an area that measures 127 (W)
⋅
63 (H) dots.
Text Screen
Graph Screen
The contents of each type of screen are stored in independent memory areas.
Press
!6
(G
T) to switch between the graph screen and text screen.
1-2-3
Display
1-2-2
Display
1-2-3
Display
5-1-1
Sample Graphs
5-1-2
Sample Graphs
20050301
5-1 Sample Graphs
k
k
k
k
k
How to draw a simple graph
(1)
Description
To draw a graph, simply input the applicable function.
Set Up
1. From the Main Menu, enter the GRAPH Mode.
Execution
2. Input the function you want to graph.
Here you would use the V-Window to specify the range and other parameters of the
graph. See 5-2-1.
3. Draw the graph.
20050301
Example
To graph
y
= 3
x
2
Procedure
1
m
GRAPH
2
dvxw
3
6
(DRAW) (or
w
)
Result Screen
# Pressing
A
while a graph is on the display
will return to the screen in step 2.
Summary of Contents for fx-9860G AU PLUS
Page 1: ...fx 9860G AU User s Guide E http edu casio com ...
Page 2: ...Important Please keep your manual and all information handy for future reference ...
Page 27: ...20050401 1 1 Keys 1 1 1 Keys ...
Page 335: ...20050401 u u u u u Input Example u u u u u Results 6 5 25 Tests ...
Page 361: ...20050401 Calculation Result Output Example p F distribution probability 6 7 15 Distribution ...
Page 435: ...20050401 8 8 2 Program Library egcw w ww w ...
Page 437: ...20050401 8 8 4 Program Library Example 1 Example 2 fw baw bf w fw baw ca w ...
Page 439: ...20050401 8 8 6 Program Library wba wb w w d ...
Page 441: ...20050401 8 8 8 Program Library dw fcde wfcde wfcde fcde w daw w 20070101 ...
Page 443: ...20050401 8 8 10 Program Library b awaw bwaw aw x d w ...
Page 590: ...CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD 6 2 Hon machi 1 chome Shibuya ku Tokyo 151 8543 Japan SA0701 E ...