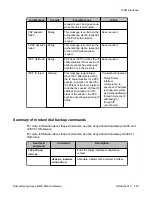
is automatically activated and the modem dials. For more information on the
backup
interface
on page 256.
• A Branch Gateway USB port can be used to support a USB modem for dial backup. Thus,
the Dialer can use the same USB modem that is used for remote access to the device.
Asynchronous dialing and modem recognition options must be set on the USB port to
support creation of the Dialer interface.
• The Dialer interface supports PAP and CHAP authentication for PPP connections. In
addition, the Dialer interface can be configured to be a member of a VPN, allowing
encryption of the modem traffic. Van Jacobsen compression is available for encrypted
traffic over the Dialer interface, allowing optimal use of bandwidth. For more information
on configuring PPP authentication and encryption, see
on page 251.
For more information on heading compression, see
Header compression configuration
on
page 234.
• It is recommended to filter traffic through the Dialer interface to permit only those packets
necessary for continued interaction with the Avaya Aura
®
Communication Manager
server. Filtering can be accomplished using access control lists, which specify traffic
permissible through a selected interface. For more information on configuring access
control lists, see
on page 557.
• Dynamic CAC can be used in conjunction with IGAR to provide a stable backup path for
continued IP phone function in the event of a dial backup scenario. Dynamic CAC notifies
the Avaya Aura
®
Communication Manager server that no bandwidth is available for bearer
traffic, keeping the dial circuit from becoming fully congested. IGAR provides a path for
gateway-to-gateway traffic destined for a remote Avaya Aura
®
Communication Manager
server by forcing voice calls to and from the branch office to use the PSTN for bearer
traffic. For more information on configuring Dynamic CAC, see
page 280. For more information on configuring IGAR, see
Administrator Guide for Avaya
Aura
®
Communication Manager
.
• Static IP addressing for the Dialer interface may not be feasible. Dynamic IP addressing
is available to enable you to connect to the remote network through an ISP. ISPs
commonly provide IP addressing for connected ports on an as-needed basis. IP
unnumbered links are available to supply addressing in situations where you wish to run
routing over your network link without committing a subnet. For information on dynamic
IP addressing, see
on page 509. For information on configuring
unnumbered IP, see
on page 426.
• Object tracking can be used with the Loopback interface to provide an alternative method
for activating the Dialer interface when connectivity with the main office is lost. This is
useful in configurations where the WAN interface is not connected directly to the Branch
Gateway. Use object tracking to configure RTRs to verify connectivity with the main office.
If the RTR fails, the object tracker can be configured to change the status of the Loopback
interface to down. If the Dialer interface is configured as the backup for the Loopback
interface, the Dialer interface will automatically dial when connectivity fails. For more
information about object tracking, see
on page 282.
WAN interfaces
Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway
October 2013 265
Summary of Contents for G430
Page 1: ...Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway Release 6 3 03 603228 Issue 5 October 2013 ...
Page 12: ...12 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 ...
Page 246: ...VoIP QoS 246 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Page 556: ...IPSec VPN 556 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...